Late last year I began experimenting with "Vibe Coding" using Claude and MCP (Model Context Protocol) Tools, I've explored this new frontier of human-computer collaboration, where the most critical skill hasn't been mastering syntax or memorizing APIs, but communicating clearly and logically in an ongoing dialog with an LLM.
Read MoreA Bicycle for the Mind
Amid the chaos of a world in crisis, I’ve found hope in an unexpected place: coding. With tools like Claude.ai and MCP, I’ve been building a web app to help food pantries serve their communities better—automating inventory, breaking language barriers, and streamlining processes. This isn’t just about code; it’s about turning anxiety into action, using technology to create something meaningful. If you’ve ever wondered how AI can amplify human effort, this is a story for you.
Read MoreVideo Lecture: 3D Modeling Basics for Beginners – Techniques, AR Tips, and Intro to AI Tools
I have some exciting news! October 23rd, 2024, I was once again invited to guest lecture at CMU School of Design. I decided to follow up with a recorded version to share. In this recording, made after the original lecture session, I cover the essentials of 3D modeling with a focus on beginner-friendly techniques. You'll find practical insights into mesh modeling, workflow tips for Blender, and an introduction to preparing models for augmented reality. The full lecture video is embedded below, followed by detailed notes that offer a step-by-step breakdown of theory and techniques for anyone new to 3D design. Dive in, explore, and start building your own 3D modeling skills.
Principles of Mesh Modeling
Note on Mesh Modeling Focus—Or Why This Lecture Focused Primarily on Mesh Modeling:
Meshes are the standard 3D model type used in real-time 3D engines—like Unity, Unreal, and virtually every AAA video game title in the last 30 years, going all the way back to Quake, by id Software in 1996.
Key Principles:
Use Quad Faces Whenever Possible: Design your shape faces with quads instead of triangles and ngons.
Reason: Quads are infinitely divisible, making it easier to adjust geometry resolution as needed. Tris and Ngons are not as flexible, which can lead to undesirable artifacts and poor topology.
3D games primarily use triangles (tris) instead of quads because triangles are the simplest polygon shape and always planar (a flat surface), making them computationally faster to render in real-time on limited hardware, which was crucial for early gaming systems underpowered computer hardware. Essentially, triangles require less processing power to calculate and display on screen compared to quads, which have more vertices and edges.
On modern computer hardware we can get away with more complex geometry, and it's generally a better trade-off to build mesh models from quads. That is, the computational costs are vastly outweighed by the benefits of evenly divisible face geometry and more manageable topology. Lastly, quads are easily converted into tris, by producing diagonal edges between the four vertices.Work from the Lowest Possible Polygon Count: Always start with the lowest polygon count (i.e., resolution) for your model. You can increase resolution later with subdivision modifiers, but it's not as easy to reduce the resolution later.
Reason: Editing a high-resolution mesh is more difficult than working with a low-resolution one, which offers greater control and flexibility. It also takes much more processing power and memory, which will slow down Blender and increase the risk of crashes.Keep Base Shapes Simple: Keep your base shapes as simple as possible. When adding details, create those elements as separate objects. When you hit a milestone, consider duplicating a model or a collection of models to a new instance for further refinement.
Reason: This approach makes 3D modeling more manageable, allowing for easier adjustments and maintaining clean geometry.Use Modifiers and Non-Destructive Editing Whenever Practical: Designing a symmetrical shape? Cut it in half and use a Mirror Modifier to cut your editing time in half. Keep in mind that the most complex designs can ultimately be derived from very basic shapes: Spheres, Cones, Toruses, and Cubes.
Work From Reference Images, Even If Just A Few Basic Sketches: Press Shift + A to open the Add menu. Navigate to Image > Reference. Select the image file you want to use from your computer. The reference image will be added to your 3D Viewport, where you can position, scale, and rotate it as needed for your modeling task.
Build The Overall Form First, and Then Separate into Smaller Objects: This will ensure that your designs are cohesive and edges are properly aligned. When you're ready to divide into separate objects, duplicate the objects into a new Collection.
Experiment, Tinker, Explore, and Start Over: You're unlikely to get the design right on the first attempt. It's often necessary to work through the problem, and then start over from scratch once you've had enough time to explore the form. Reason: Your second draft will almost certainly be better than the first.
Blender Quality of Life Recommendations:
Save Your Project Files Early and Often: Use Blender's "Save Incremental" (⌥+⌘+S) (Option + Command + S) to manage version control. Doing this will give you the freedom to fearlessly tinker and explore (as mentioned in the previous point) before settling on a final design.
Crank Up The Number of Undo Steps: Open Edit from the top menu. Select Preferences to open the Blender Preferences window. In the Preferences window, click on the System tab. Scroll down to find theUndo Steps setting.
Increase the value (the default is 32). If you have enough system memory, set it to 256 for more flexibility in undoing actions. Close the Preferences window to save your changes.
Consider Using A Material Library: Blender has a basic built-in material library, but it's not very useful. Look into large libraries, such as PBR Material Asset Library + OneClick Add-on for Blender (https://shardsofred.gumroad.com/l/CfOnY). Creative Commons License (CC0) materials can be used for basically anything, and will save you time.
Remember to Perform a UV Unwrap on Your Model Geometry for Best Results When Texturing: The most realistic textures in the world won't help you if your model doesn't have good UV Mapping. Remember the chocolate Santa Claus example? Proper wrapping is essential for creating realism with your models. https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/ modeling/meshes/uv/applying_image.html
Recommended Extensions and Add-ons:
VDM Brush Baker: Helps you create and bake Vector Displacement Maps directly in Blender.
Bool Tool: Boolean operations for complex shape creation.
Node Wrangler: Enhances node editing management.
Rigify: Automated rigging solution for character animation.
Loop Tools: Useful for organic modeling (with some bugs appearing
in Blender 4.2—be sure to keep this add-on updated!).
Other Useful Add-ons: Auto Mirror, F2, Extra Mesh/Curve Objects, Extra
Grease Pencil Tools, Copy Attributes Menu, and MeasureIt.
Bonus: Need furniture? Most of IKEA's catalog of products have 3D models available. Search for "IKEA" under Extensions and you can easily search and import 3D models into your scenes.
Note: Ensure 'Allow Online Access' is enabled in Blender's System Preferences for add-on updates.
Create Augmented Reality Experiences for iOS with Xcode Developer Tools, Reality Composer, and USDZ File Format
Once you've finalized your form, added necessary details, and applied your materials, you should be ready to export your model.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Preparing 3D Assets for Export to USDZ:
Duplicate Your 3D Assets and Collections: Create a new instance of your 3D assets specifically for export.
Apply All Transforms: Hit A to select all visible objects, then press ⌘ + A (Command + A) and select All Transforms to apply.
Apply All Modifiers: Apply all modifiers in the same order they were added to each model—except for subdivision, as tessellation data can (usually) be included without applying it directly to the models.
Join All Components: Hit A to select all visible objects, then press ⌘ + J (Command + J) to perform a join operation.
Export the File: Go to File > Export > Universal Scene Description (usd*).
Configure Export Settings:
Include: Check Visible Only and Selected Only.
Blender Data: Select Custom Data.
Namespace: Use the default setting (UserProperties).
Blender Names: Enable this option.
File References: Set to Relative Path.
Convert Orientation:
Z = Forward Axis
Y = Up Axis
Note: Many other 3D tools, including Xcode's tools, interpret 3D models with a different axis orientation than Blender. If you don't apply this conversion, you'll find your model improperly rotated following import. If this happens to you, double-check these settings.
Use Settings for Render: Enable this option.
Object Types: Select Mesh, Volumes, Curves.
Geometry: Enable UV Maps, Rename UV Maps, Normals.
Subdivision: Set to Best Match.
Rigging: Enable Armatures (if you have rigged and animated your
model).
Materials: Select USD Preview Surface Network and Export Textures.
USDZ Texture Downsampling: Set to 1024px or up to 2048px (the
largest size acceptable for iOS QuickLook).
Update File Extension: Change the export file name extension
from .usdc to .usdz.
If no issues are encountered after export, you should be able to view your model in Augmented Reality on any iOS device. Open your exported file from iCloud, send it as an email, text, or AirDrop to another device to view.
Setting Up Xcode and Reality Composer:
The latest version of Xcode doesn't include Reality Composer, as Apple has shifted their focus to the Vision Pro. You can still access the Augmented Reality Tools for iOS devices, with some additional steps.
Step-by-Step Instructions:
Download the Latest Version of Xcode 14: Download from the provided
link: https://developer.apple.com/download/all/
NOTE: You'll need to create an Apple Developer Account (it's free) to access the above link, or using this direct link: https://download.developer.apple.com/Developer_Tools/Xcode_14.3.1/Xcode_14.3.1.xip
Extract and Rename The Older Version of Xcode: Rename Xcode.app to Xcode14.app and place it in your Applications folder.
Open Terminal on Your Mac.
Open the Applications Folder in Finder.
Drag the Xcode14 App into Terminal: This will automatically add its path.
Add to the Path: Next to the path, add: /Contents/MacOS/Xcode.
Full Command Example: The command will look like:
/Applications/Xcode14.app/Contents/MacOS/Xcode
Run the Command: Press Enter to run the command.
You should now have access to Reality Composer in Xcode. Click on the Xcode menu on the task bar, then click Open Developer Tool, and then click on Reality Composer.
Learn more about using Reality Composer here: https://developer.apple.com/documentation/realitykit/realitykit-reality-composer
Learn more about Apple Reality Kit and ARKit here: https://developer.apple.com/augmented-reality/tools/
BONUS: Generative AI and 3D
Tripo AI (https://www.tripo3d.ai/app) is an advanced generative AI tool that allows for both text-to-3D and image-to-3D model generation. This tool offers users an intuitive way to create complex 3D assets with minimal manual input, simply by describing what they need or providing a reference image.
Key features:
Text-to-3D and Image-to-3D Conversion: Users can input a detailed description or upload an image, and within seconds, the AI generates a draft model ready for refinement.
Prompt: "A pineapple-hedgehog with spiky fruit armor and leafy quills."
https://tripo3d.ai/preview?share=9a57357e-6262-469c-afb1-c7af74d92c93
Prompt: "A 1980s sci-fi robot stylized as a Nintendo NES product."
https://tripo3d.ai/preview?share=a08a55cd-9e66-48a5-be3d-85a26160e461
High-Speed Generation: Tripo’s AI processes are optimized for efficiency, allowing users to generate detailed models in a matter of seconds, ideal for prototyping or quick visualizations.
Customization Tools: After generating a model, users can adjust topology for increased details, or apply stylization, such as voxels.
Seamless Integration: Tripo3D supports a variety of export formats like .usdz .obj and .fbx, making it easy to import models into Blender and other software for further editing.
Generate full texture maps with PBRs: includes generation of PBR textures, adding even greater details beyond the geometry.
Automatic rigging and basic animations: Applies a basic animation rig to generated models and simple animations, such as a running character, to the model geometry.
Downsides:
Imprecise generation: just like AI image generators, results are unpredictable and often wrong.
Costs: Using this tool will require a membership plan, and has limited monthly credits, which limits usage.
CREDITS:
Thanks to all of these wonderful educators and content creators who continue to inform and inspire me throughout my 3D journey. Preparing this lecture required lots of time and consideration for how to condense what I’ve learned over the last five years into something I could demonstrate in under 2 hours. This wasn’t easy, but I had many fantastic resources to pull from.
If I’ve left anyone out, please leave a comment so I can include them here:
Ashley Deal and Raelynn O'Leary — CMU School of Design Faculty and Founding Partners at Dezudio http://www.dezudio.com
Phil Eichmiller — Principal Software Engineer at Autodesk: https://blogs.autodesk.com/community-journal/2022/04/26/meet-phil-eichmiller-principal-software-engineer/
YouTube Creators:
Reference Files:
Robot model created with Tripo AI
Robot model with corrected orientation
Note: Due to a bug, the robot walking animation doesn’t playback in QuickLook AR for iOS.
HAVE QUESTIONS? ASK PHIL
Have questions about CAD, Fusion 360, or the Portland maker scene? Ask Phil! He’s a Principal Software Engineer at Autodesk, inc. and teaches CAD at Portland Community College. He’s also the host of Community Conversations series: Getting started with 3D modeling in Fusion 360
You can reach him at phil.eichmiller@autodesk.com
Phil Eichmiller — Principal Software Engineer at Autodesk, Inc.
These links were kindly provided by Phil. I’m posting them here for visibility.
Starting with basics
https://www.autodesk.com/autodesk-university/class/Design-just-12-commands-essential-modeling-commands-Fusion-360-2022
Sketch knowledge
Parametric excellence
TUTORIAL: How to use ultra realistic Quixel Mixer materials with Fusion 360 [Part 2]
Welcome back! In Part 2, we’ll explore adding Quixel Materials to your designs in Fusion 360 and setting up a rendering scene. If you haven’t already, review Part 1 and install Quixel Mixer. You’ll want to create and export a mix for use in Fusion 360 prior to the steps in this tutorial, or download an example material set here.
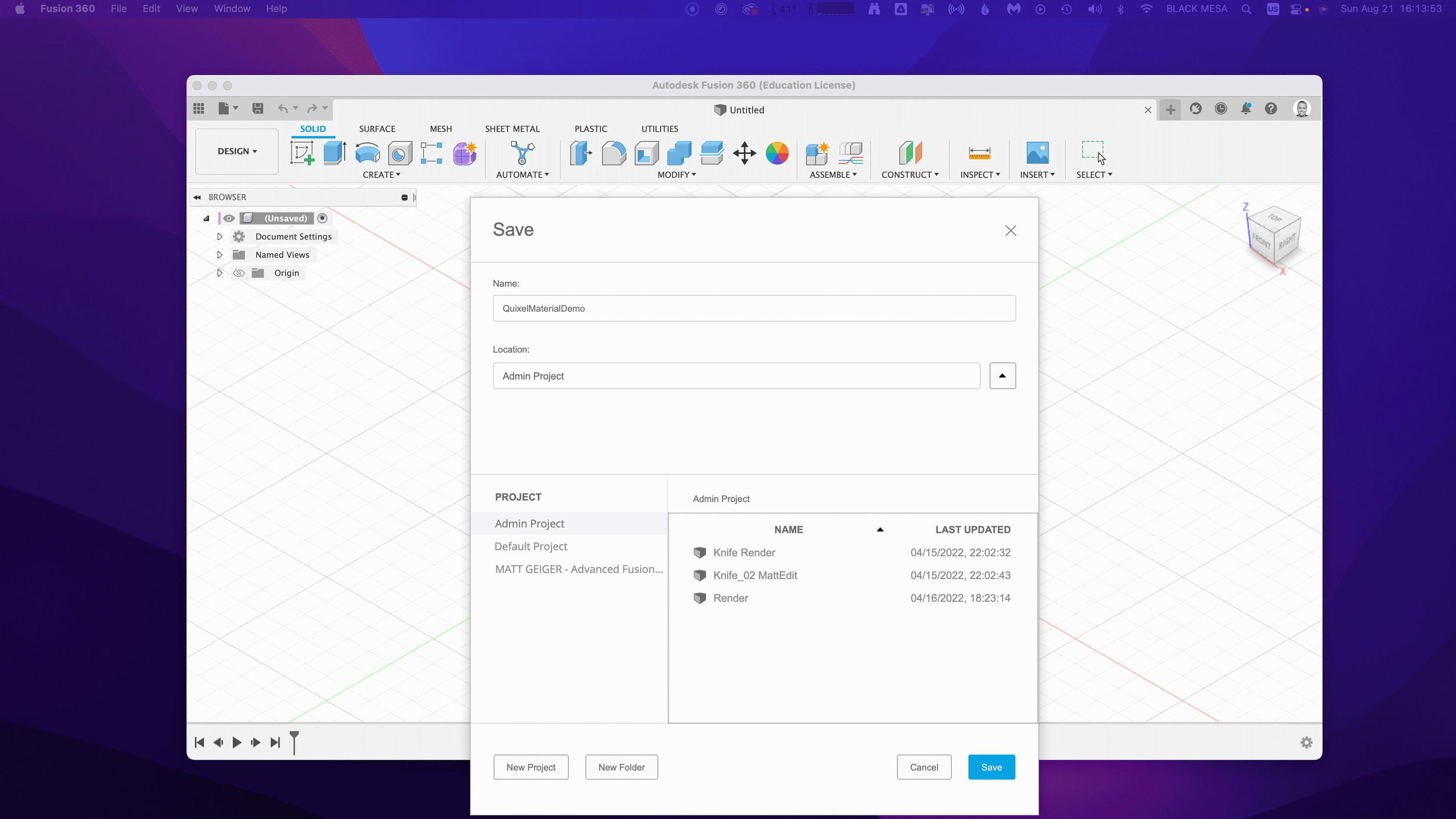
First, let’s create a new project in Fusion 360:
Creating a new Fusion 360 Project
After you open Fusion 360, Click “Save” and give your project a name. In this example I used “QuixelMaterialDemo.”
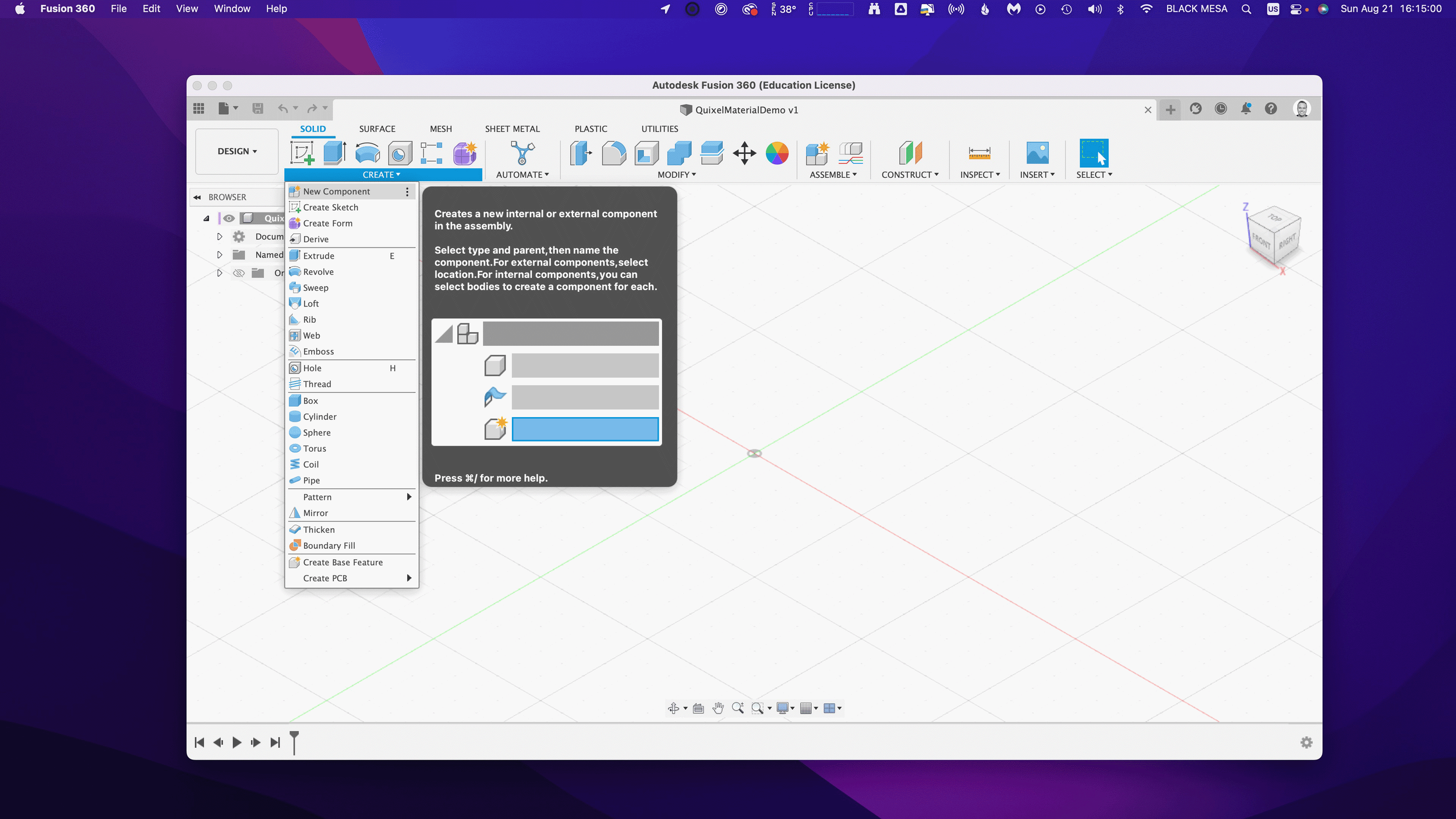
After you save your project, we’ll want to create a new component and make it active.
2. Create a new Component
This is generally a good practice with Fusion 360, because we can more easily manage changes made to the design when the timeline is broken up by individual component histories. Name your component “Floor” and then make sure “Activate” is selected (should be by default), click “OK” to continue.
Next, we’ll want to create a sketch to define the floor’s dimensions. Click “Create” and make a Center Rectangle on the bottom plane.
3. Create a Floor
Make your sketch 3 meters x 3 meters in size, with the Origin at the center. Click “Finish Sketch” to continue. If you’ve done everything right, then you should have a sketch that is fully constrained (i.e., you’ll see black lines instead of blue lines for the outer dimensions of your sketch).
Next, we’ll extrude the sketch below the plain. This will create a new body, based on our sketch dimensions.
Click Create and then Extrude. Then, extrude the sketch -1mm below the plane and click “OK.”
Next, Save the design. You’ve created your first body and now would be a good time to save your progress.
Note the reason for your save and Click “OK.”
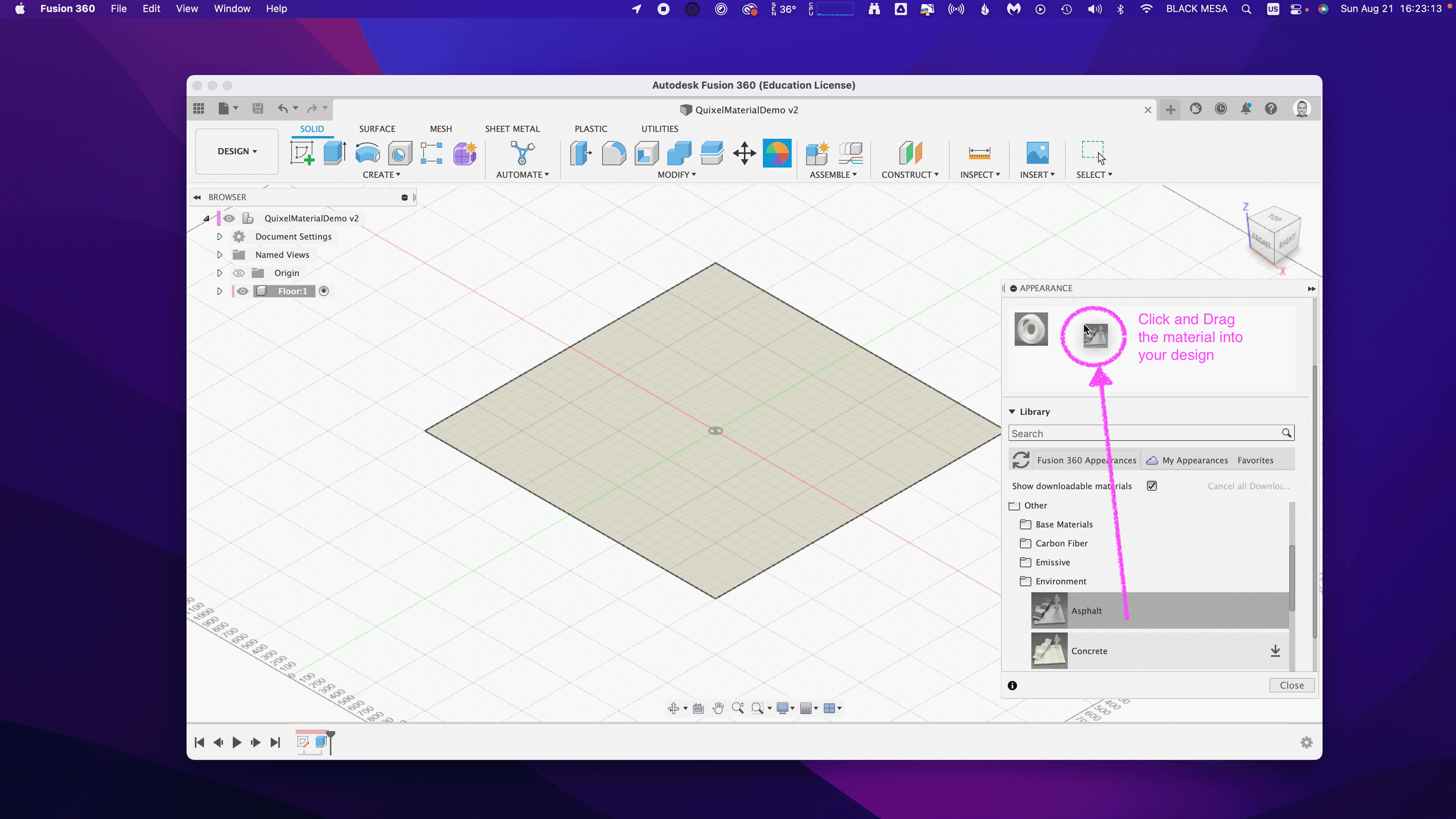
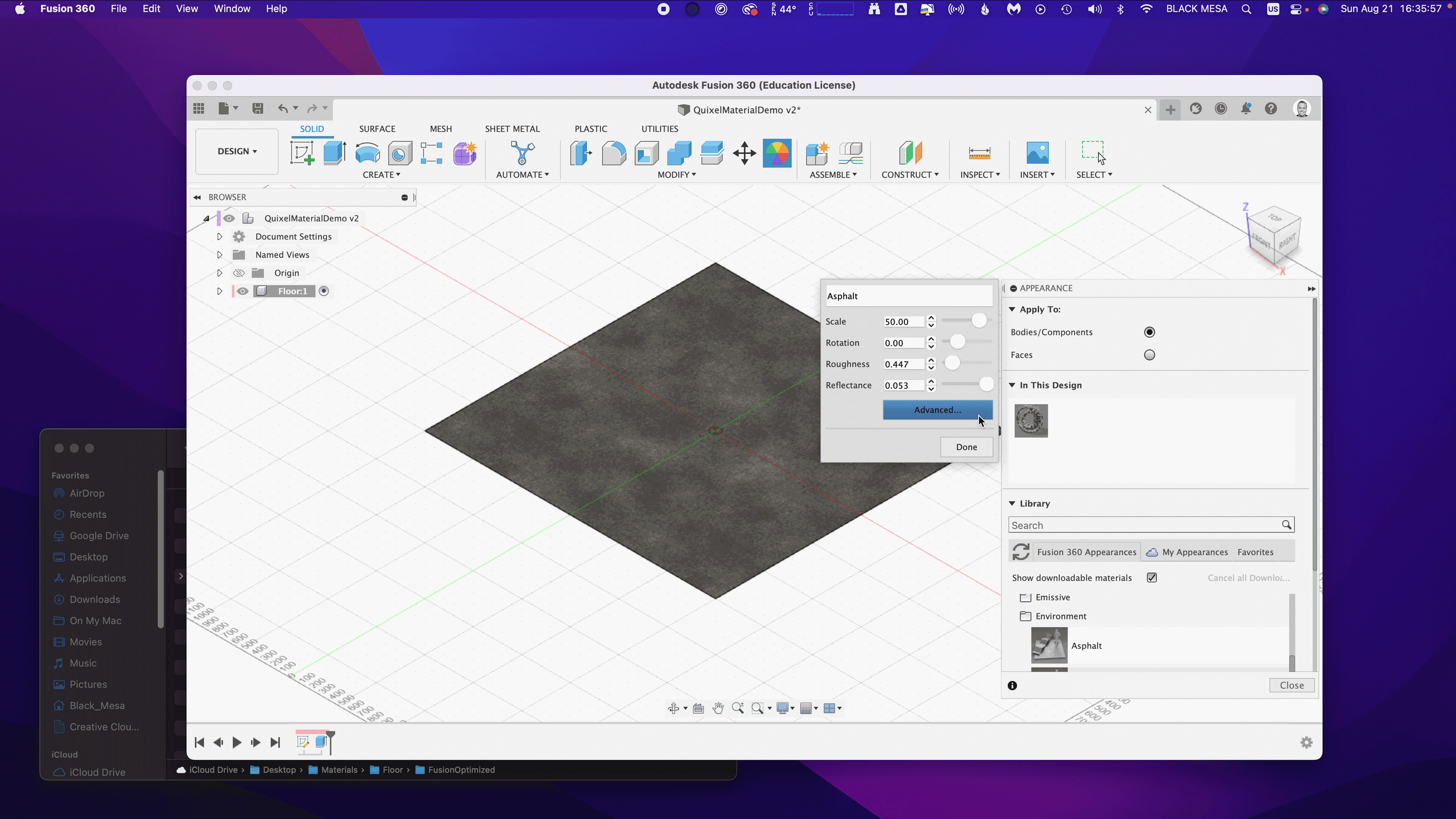
Next, we’ll want to change the Appearance of our floor. Click Modify Appearance to bring up the Appearance Window.
4. Add material
Here we can see the default material for the Floor body. We’ll want to replace that material with our Quixel Mix. To do that, let’s start by downloading a similar material.
Note: in general, you’ll find it is easier to add Quixel Mixer materials when you adapt an existing material in Fusion 360 with similar attributes. In this case, we can use the existing Asphalt Material.
After the download finishes, click and drag the Asphalt material into your design.
We can then replace the default material with the Asphalt.
5. Replace Fusion 360 Material with Quixel Mix
Next, we can begin modifying the Fusion 360 Asphalt material with the Quixel Mix.
As mentioned in Part I, the materials in Fusion 360 are made up of individual map image files:
Albedo/Diffusion/Color — the color a material reflects
Normal and/or Height Maps — the bumps and imperfections along a surface
Roughness — the smoothness of a surface (ranging from a sharp reflection to fuzzy/diffuse)
Reflectance/Specular/Metalness — the reflectiveness of a surface (ranging from mirror finish to a dull surface)
Anisotropy/Ambient Occlusion — the shadows along a surface
Refractive —how light bends through a surface
Emissive — how much light a surface emits (glow)
Translucency/Opacity — how transparent a surface is to light
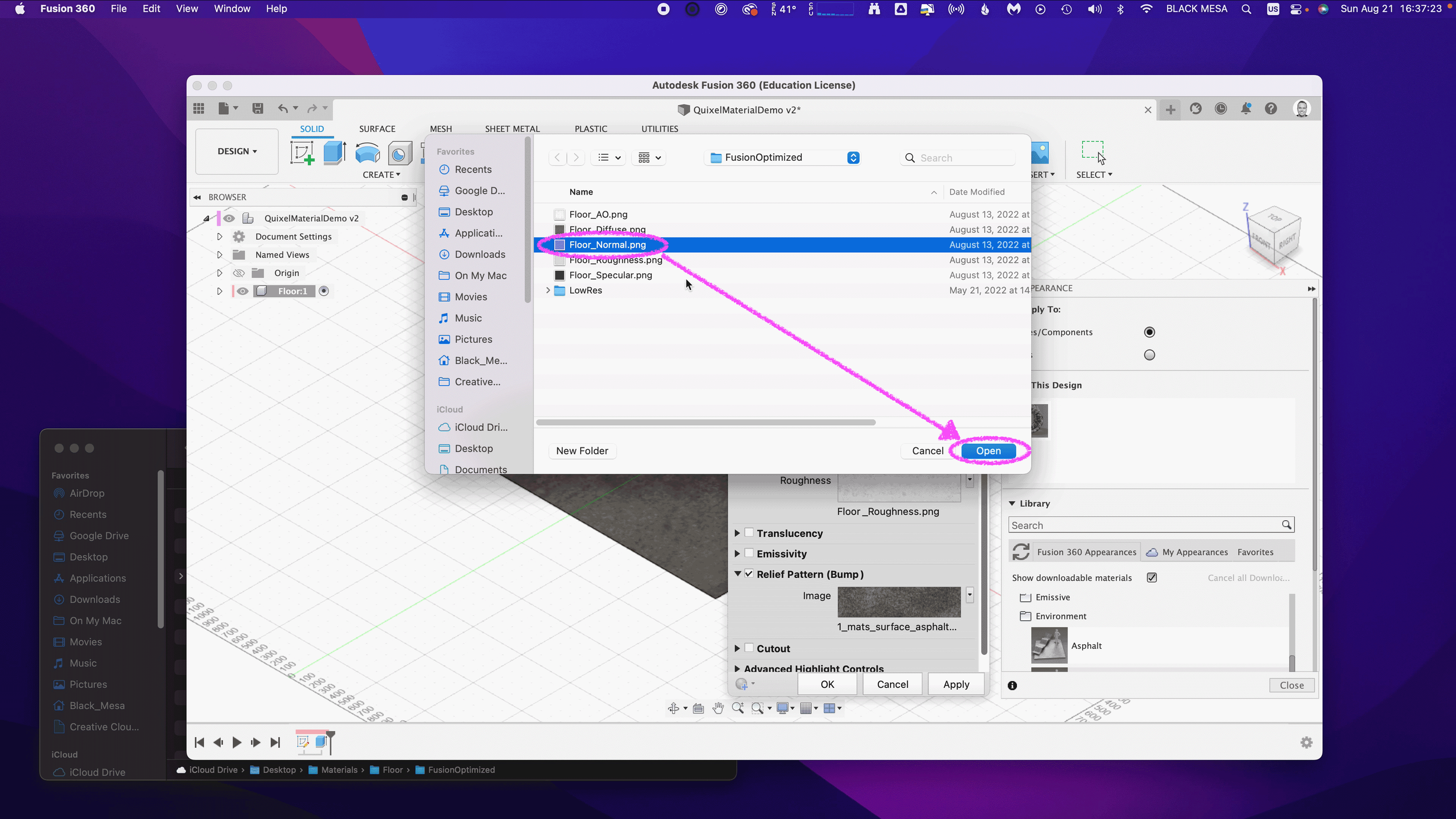
If you’re using the included sample images, you’ll find some but not all of these maps. Depending on what materials you’re mixing, you’ll need different image maps. The sample image package includes:
Floor_Diffuse.png — Color (placed in Parameters)
Floor_Roughness.png — Roughness (placed in Parameters)
Floor_Specular.png — Reflectance (placed in Parameters)
Floor_Normal.png — Normal (placed in Relief Pattern (Bump))
Floor_AO.png — Anisotropy (placed in Advanced Highlight Controls)
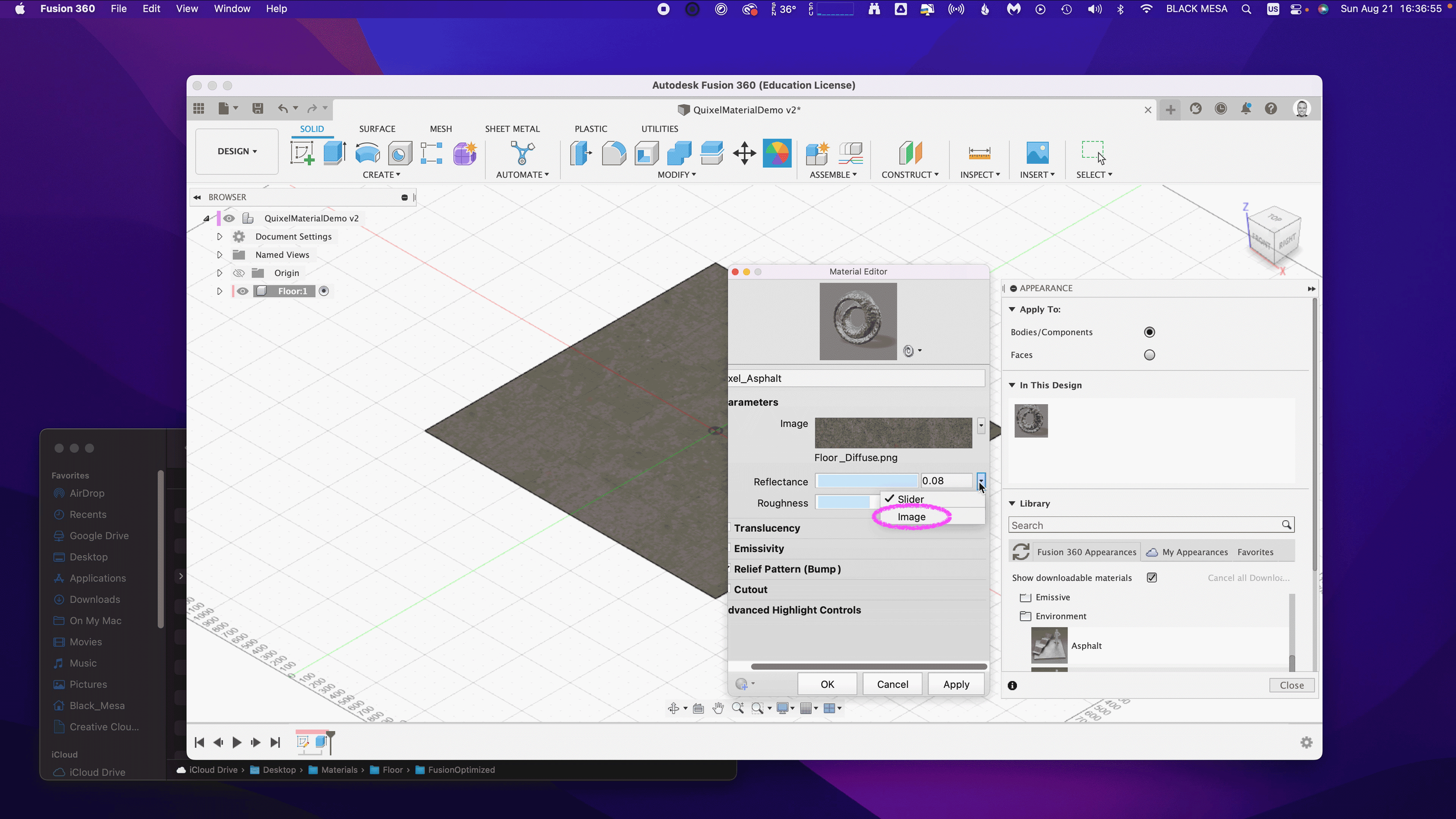
By replacing and adding these map files to the Fusion 360 Asphalt material, you can transform it to the Quixel mix. To start this replacement process, open the Appearance window, double-click the Asphalt material and then click “Advanced…”
Rename the material to “Quixel_Asphalt” to distinguish the material from the original Fusion 360 Asphalt.
Under Parameters, we can add three (3) image maps. First, we’ll apply the diffusion/color map to the Image input in Fusion 360. Click on the Image filename 1_mats_surface_asphalt_color.jpg and navigate to your replacement images.
Select your Albedo/Color/Diffuse map file. If you’re using the sample images, it’s the file named Floor_Diffuse.png. Click Open to replace the default image file.
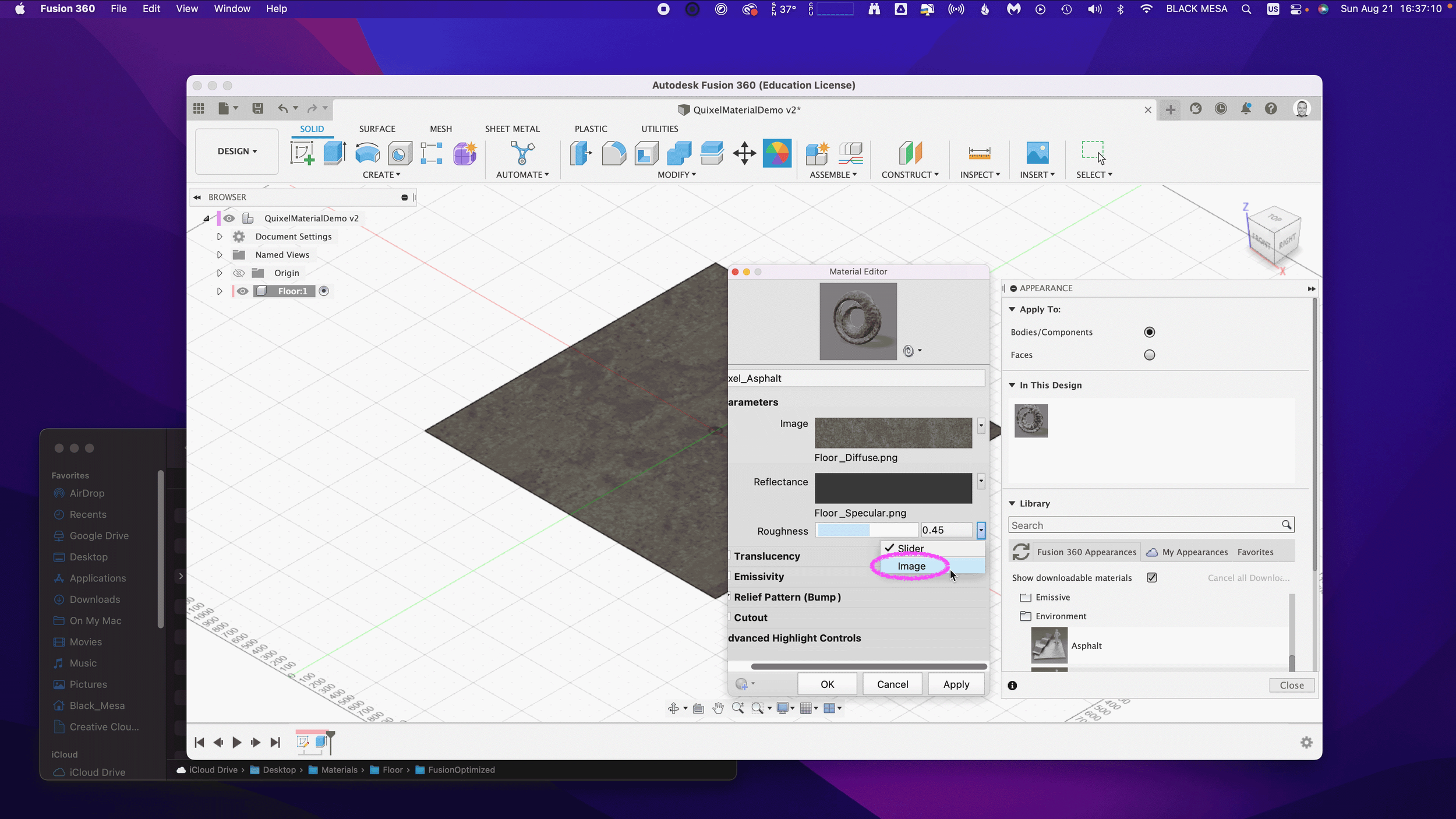
Next, we’ll repeat the process with the Reflectance and Roughness maps. By default, these two material attributes are set as Slider values, click the drop down arrow and then select Image to replace the slider value with an image map.
Next, select the Metallic/Specular image map if you’re using the sample images, select Floor_Specular.png and click Open.
Next, repeat the same steps for the Roughness value. Select Image and then select your Roughness Map. If you’re using the sample images, select the Floor_Roughness.png.
Now that we’ve completed the three Parameter maps, we can move on to the Relief Pattern (Bump) map. Once again, we’ll replace the default image file (1_mats_surface_asphalt_.jpg) associated with the material. Note: Fusion 360 supports both bump and normal maps. If you want to know more about these two approaches to texturing a 3D model, then click here.
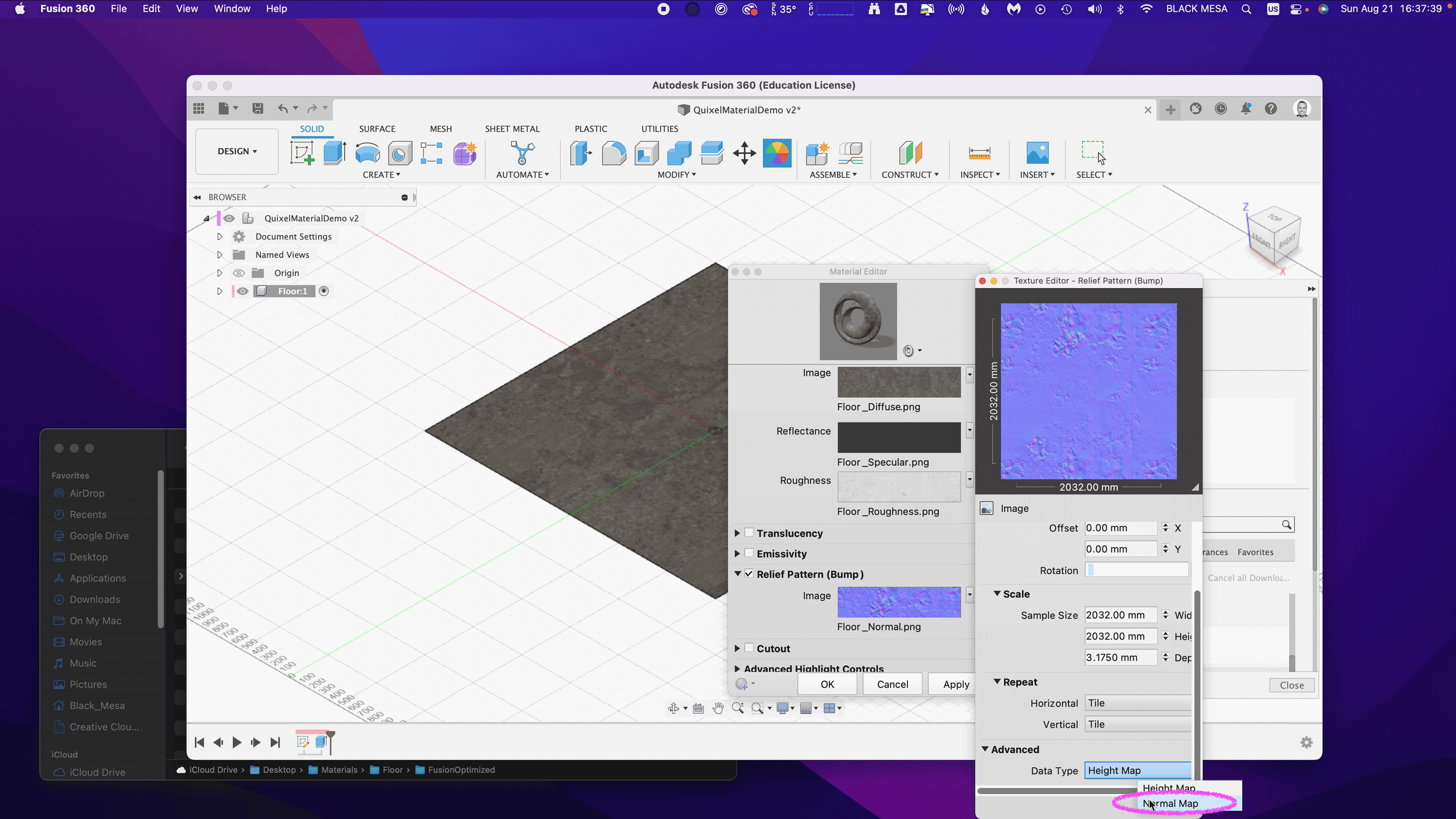
Next, we need to change the Relief Pattern from a Height Map to a Normal Map. To do this, we need to Edit the image.
Next, scroll down to Advanced and change Data Type to Normal Map.
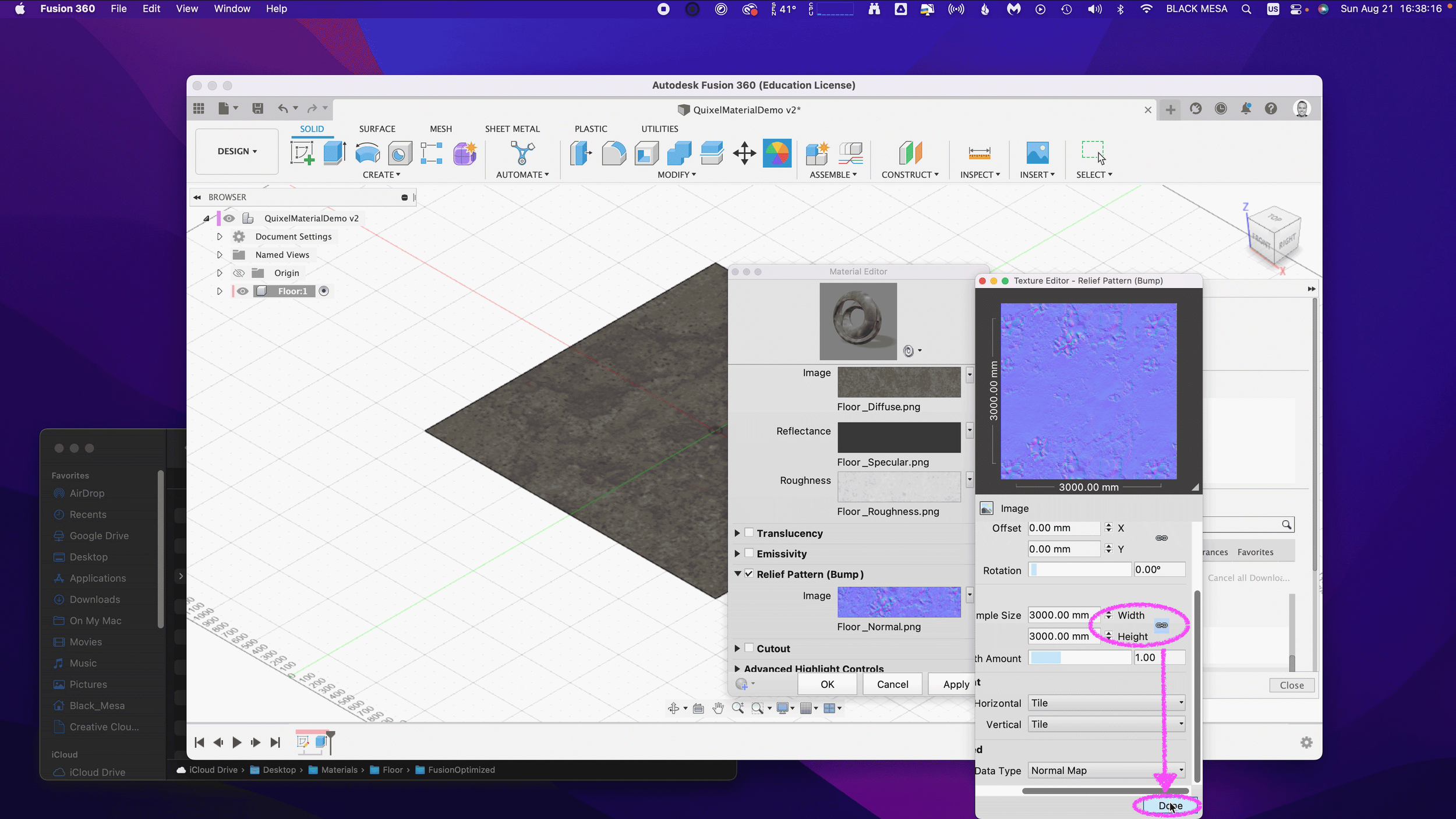
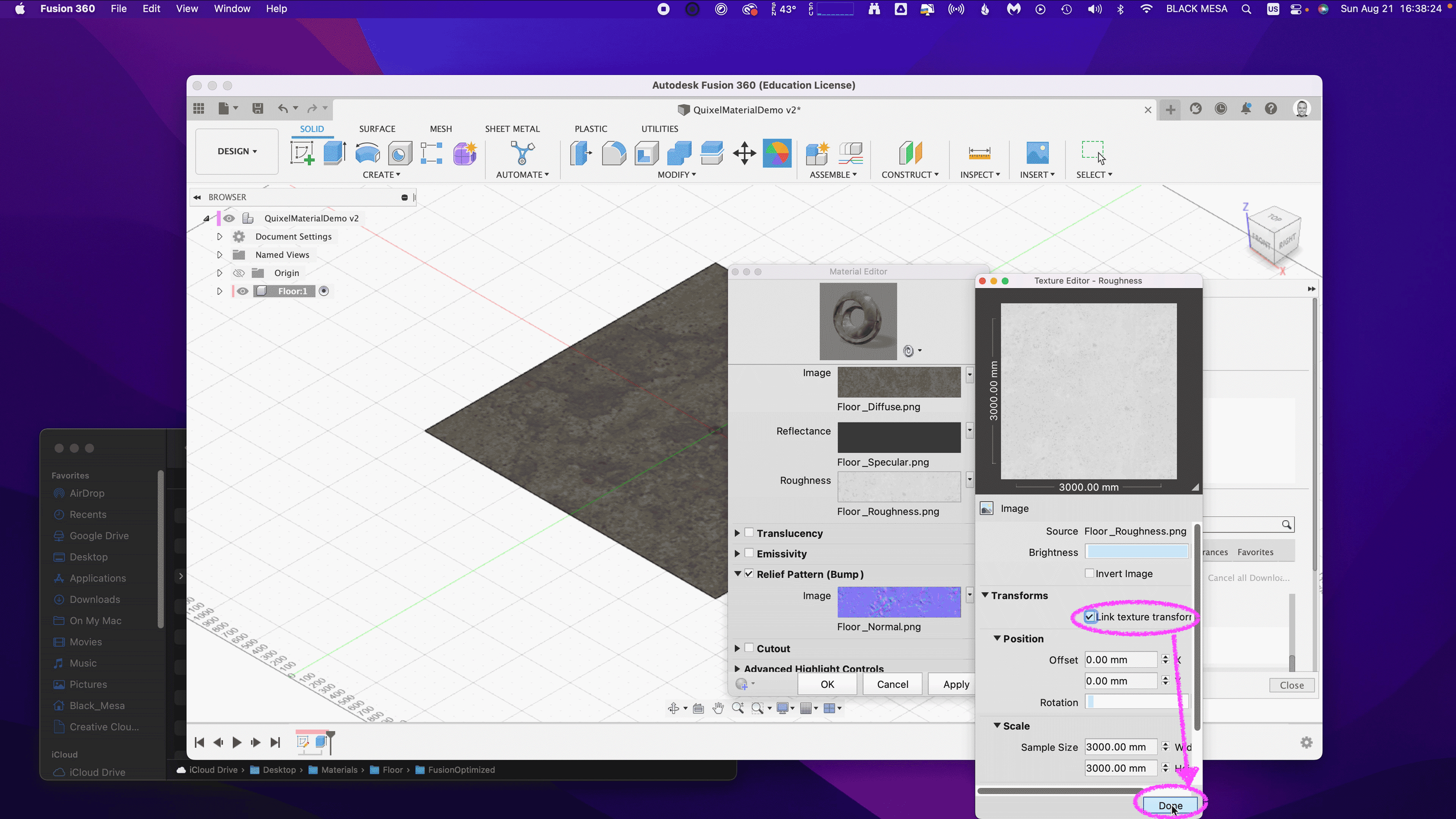
Next, we need to ensure that all of our maps are using the same Sample Size. Be sure to repeat this step for all image maps. We also need to ensure that all of our Maps have Linked texture transforms. Check the Link texture transforms under the Transforms section of the Texture Editor. Be sure to repeat this step for all image maps.
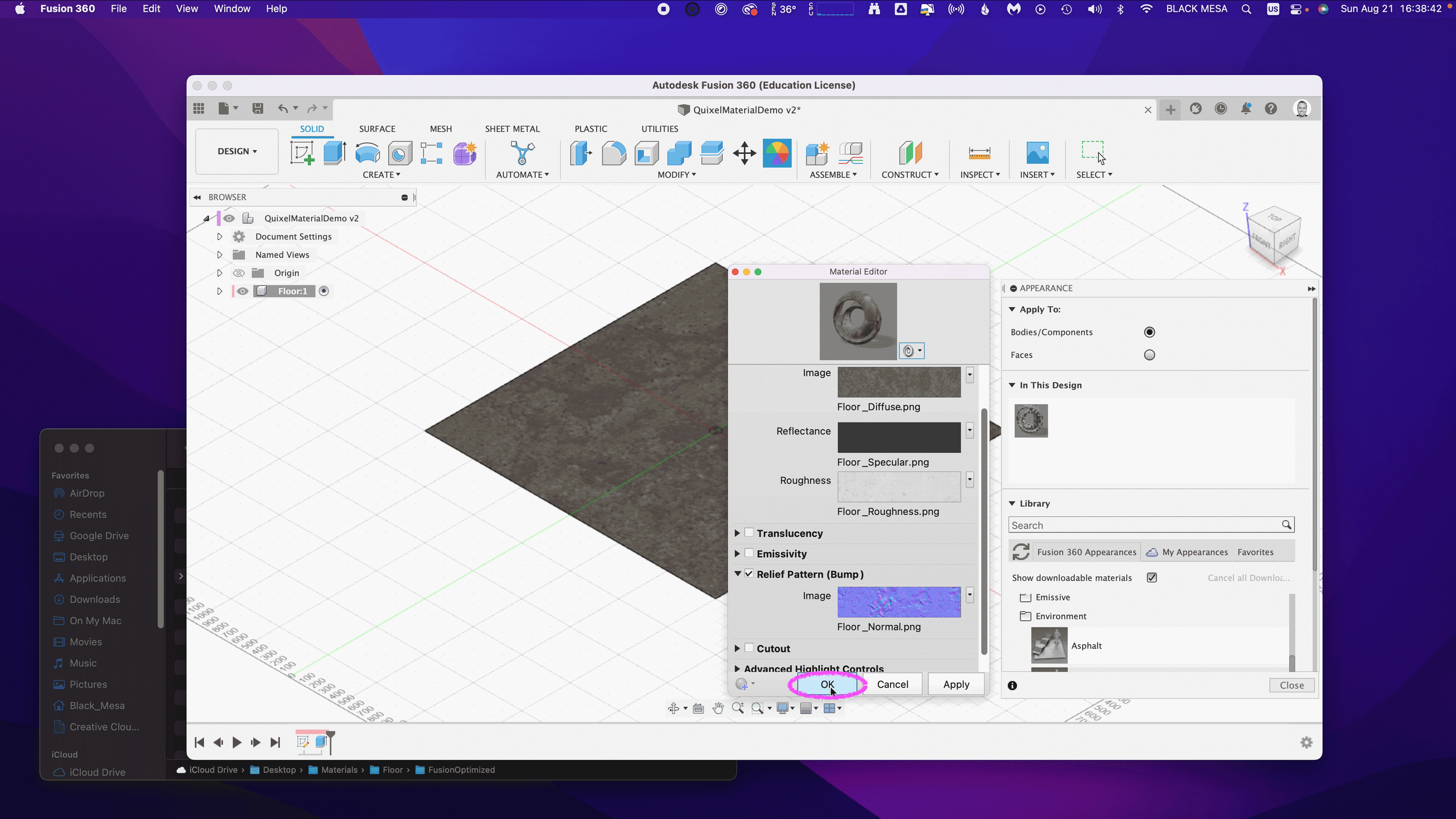
These steps are important, because they ensure that all of the image map data are aligned equally to the material in Fusion 360. After you’ve verified these settings, you can click “OK” to finalize the changes to this material.
Now that the material has been updated you can Close the Appearances window.
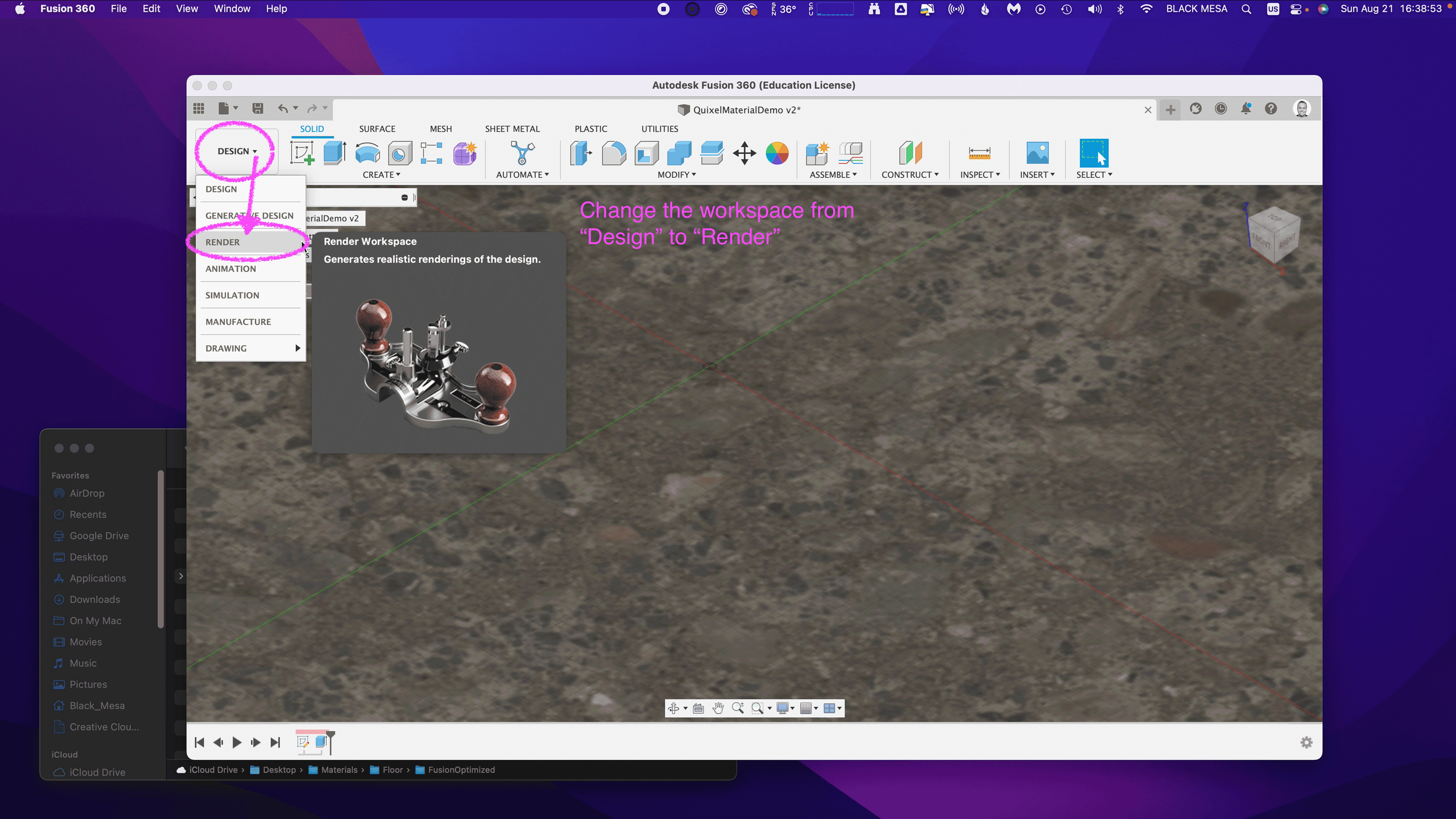
To check and validate our new material, we need to switch to the Render Workspace in Fusion 360. Click on the Workspace button, and change it from DESIGN to RENDER.
6. Test render scene
Next, let’s save the design to capture the new material settings in your Fusion 360 Timeline. Click File and Save.
Fusion 360 will prompt you to describe your save point. Let’s name this save “Quixel Material Added” and click OK.
Before we can test our new material, we need to edit the SCENE SETTINGS from the SETUP Menu. Open the SCENE SETTING Window and Click+Drag “Dry lake bed” to the Current Environment and then Click Close.
We also need to change the IN-CANVAS RENDER settings to FAST, so that we can easily see the material’s performance during rendering. To do this, click on the IN-CANVAS RENDER SETTINGS icon and Click on the Fast tab. Then, Click OK to update the rendering method.
Next, we can preview the rendering, and see how the various maps work together under different lighting conditions. To do this, start the In-Canvas Rendering and then open Scene Settings, click on the Position Icon to bring up the Rotation and Scale Sliders. By changing the rotation, you can see how the surface of your floor object casts shadows at different angles, corresponding to the surface material.
Make sure to save your project to retain your rendering settings. If you’ve made it this far, then congratulations! You now have all of the information necessary to import Quixel Mixer materials in Fusion 360. In Part 3, we’ll explore some techniques for applying these materials to complex geometries, and how to post-process your images for additional realness. In Part 4, we’ll take these realistic models and generate Augmented Reality experiences for iOS.
Stay tuned!
Core77 Design Awards 2022
I’m very pleased to see Stuart Candy’s project “Imagination is a Commons” is the winner for Core77’s award for Speculative Design, 2022. Back in March of 2021, I received a somewhat unusual paid request — for studio photography services. One year into the COVID-19 pandemic, when vaccines were still out of reach for many, and facilities and institutions remained shuttered, I was suffering from cabin fever isolation and grieving the death of my uncle.
I was finishing up my second Master’s degree, and Pittsburgh had only begun to thaw after a long and difficult winter. Without access to the campus photography studio, Stuart had reached out to his network at Carnegie Mellon, seeking alternatives. As luck would have it, during my undergraduate studies I invested in my own studio photography setup.
My barebones digital photography setup
Scrappy resilience was a constant theme throughout 2020. Students without studio space were constantly finding ways to make do. This was one of those rare moments where few compromises were necessary, and I had everything I needed on hand. Imagine my surprise when I was handed a bag full of artifacts from the future…
T-shirts from a coding festival in the year 2030
Social distancing and staying home (for the better part of a year) had distorted my sense of time. In the first year of the pandemic, there were days and weeks that seemed to vaporize, and weekends that lasted a month. To hold these artifacts, and to focus on them through a viewfinder, I felt as though I had stepped completely outside of time and space. This was a perfect diversion from my mundane existence, and a reminder that this too shall pass.
Thank you, Stuart and Ceda. And congratulations!
Week 3 and 4 Update: 3D content migration woes
This update is coming in late, as I’ve been trying to come up with some way to explain the difficulties I’m facing with this project, while also respecting the privacy and IP. I’m leaning heavy on metaphor, but…
Imagine there are three people sitting at a bar. One of them speaks Dutch, English, and German (but only okay German, not great). Another speaks Spanish, some English (okay-ish grammar, few nouns), and fluent German. The last person at the table is a little bit unusual. They’re a rapper from Japan, they speak fluent Japanese and a little English. As a child they were an exchange student in Germany, but they’ve forgotten most of what they learned. The rapper also insists on speaking-as-quickly-as-their-mouth-can-run. They never slow down. Speed is everything.
They all have some overlap, however imperfect, in their spoken languages, but none can understand each other perfectly. This is what it feels like to develop assets for a still-in-beta realtime engine, while leveraging a parametric modeler, an open source 3D creator tool, and adhering to standards from a professional VFX and CGI-specific 3D tool.
This week my primary focus has been on getting Blender and Unreal Engine to talk to each other. Unreal prefers FBX file format (Autodesk Maya Native). Blender can export most data in this format, but there are a few catches:
No shape keys
Subdivision data is limited to a single iteration
Dynamic animation can only be exported with baked physics, and is limited to vertices and face transformations (kind of, depending on what you’re doing).
Additionally, Unreal doesn’t quite understand Blender’s material system. It will still export textures and UV map data, but you’ll need to build the material blueprint to recreate whatever you have in Blender. It is far from being a 1:1 exchange.
There are also a many weird quirks:
In Blender, the default units are meters. In Unreal, the default unit is centimeters. Before exporting from Blender, you need to set Unit Scale to 0.01. If you switch units in Blender to centimeters and leave the Unit Scale at the default of 1.0, then you’ll experience strange anomalies for things like collider bodies, skeleton mesh, etc..
In naming the rigging elements (IK skeletons, etc.), you DO NOT name any bones “root,” because Unreal will assume a hierarchy which may differ from your hierarchy (parenting) in Blender. However, you may rename the Armature container to “root” to conform to Unreal’s hierarchy.
Lastly, the only rigging data that reliably translates between Blender and Unreal Engine are deform bones and baked animations/transformations.
I’ve reached a stumbling block with my current 3D character. I can rig the character to animate, and even output that data in a manner which Unreal Engine can interpret. This comes at the expense of a vital visual element that was procedurally generated. What comes next is a difficult choice:
I can either integrate procedurally generated elements into a single mesh geometry (potentially compromising some rendering performance and visual fidelity) but without having to rework existing animation and rigging, or I can attempt to recreate the procedural mesh instancing I developed inside Blender but natively within Unreal. The former will be labor intensive, but I understand the tools well enough to work consistently toward a known output. The latter involves many unknowns, but I will also gain a deeper understanding of workflows within Unreal Engine. I’m attracted to this latter option, but I don’t know if it is best for the client and their expectations.
Week 15: Final Project Update
This will be my final update for the Studio II project. I feel a complex blend of emotions as I write this. I am relieved to be done. I am also sad to know that my time with this team has come to an end. I consider myself incredibly lucky to have spent so much time working with some truly amazing designers. I don’t know if I will ever experience anything like this again, but I hope so.
Remote collaboration has few perks, and I was lucky to be working with folks who helped to make this experience so much fun
The work we have done this week feels different for many reasons. We had to prepare something for a large and diverse audience, not all of which knew or were familiar with the context of our work. Additionally, we also needed to use this time to tie up remaining loose ends—we needed to reach an end state where our process could feel somewhat conclusive.
Our efforts were just as collaborative as ever, as we divided up the labor of our remaining tasks. I was incredibly reassuring to know my team members strengths and capabilities. Knowing who was working on a particular task was reassuring. For my part, I was busy scrubbing through a timeline in After Effects, rapidly assembling visual representations and edited footage to make a convincing newscast from the future. Considering the constraints of remote collaboration, I’m very pleased with the final product.
I have continued to ruminate about over this notion that the future is something we cannot predict, but rather something we build through imperfect knowledge. I question the power our team has to influence this process, not because I lack the confidence in our shared abilities —as I said earlier and often, I’ve been working with an amazing team— but more of a concern around consequences of inspiration. Our process was far from perfect. The vagaries of a pandemic distorted every effort. The educators we sought to connect with were terribly busy. Our own team suffered from fatigue and sleeplessness as we juggled future careers and other academic expectations. The complexity of this topic is well beyond the scope of fifteen weeks of diligent inquiry.
I cannot speak for the entire team, but I know that for me personally our exploratory research was the most intimidating phase. It was immediately clear that we were engaging in a very difficult problem. Education intersects with so many other areas of study. It is a problem of policy, culture, funding, methodologies, and it is weighed down by a history of systemic inequality and racism. Generative research methods were the biggest surprise. I was astonished by what could be gleaned through a participatory process. Including educators in the generation of concepts was exciting, and I wish we had more time to engage in this work.
Our final concepts are a reflection of many perspectives and early prototypes generated by K-12 educators
Every phase also felt too short. We needed to move on before we could fully digest what we were learning. Nevertheless, I stand behind the work we have done, because I know it represents the best we had to offer. I’ve known that design is a messy process long before my time at CMU, but I now have a much clearer sense of what it means to engage with that mess and to assemble something coherent. This work is not easy, and it is never, ever truly complete. The deadlines for a design project function like the layers of silt in a fossil record. The strata of every layer represents a progression with no clear ending or beginning. We can always dig deeper.
I hope these artifacts will inspire others as they have inspired us.
Our team has assembled a project homepage. There you will find more comprehensive information about this work, the final outcome and documentation. Check it out!
Week 14 update: The Late Edition
The final push is now upon us. This past week I’ve been working nearly around the clock with my team, pushing to bring about our future vision. One of the most labor intensive, yet rewarding parts of this project has been the production of a newscast from the future. We’ve made countless script revisions, scraped stock images, sound, footage, and crafted motion graphics elements to bring this story to life. It’s been challenging, but I’m excited to see the final results.
What’s working: our approach to generating a video is deeply grounded in research. We’re incorporating concepts generated with participants — public educators who so generously gave us their time and perspectives on the present and future state of teaching in American schools. We’re also building our story to represent several systems-level shifts, including national legislation, teachers union contracts, and individual school reforms. We used several different futuring frameworks to develop these narratives, including: cone of possibility, backcasting, STEEP+V, Multilevel Perspective mapping, affinity mapping, and worldview filters.
This process has been anything but precise. The future is something we build, not something we predict through careful measurements of trends. Understanding this truth has been very reassuring. Now that we are approaching a conclusion, I feel as though I have been on a long drive through undeveloped territory. The daylight of exploratory research gave way to the twilight of generative research and in the pitch of night we evaluated concepts. With only one headlight, we squinted off into the distance, to read the signs. Sometimes the precipitation of a pandemic obscured everything, but we relished the intermittent moments of clarity.
Those latter kinds of moment were by far the most exciting. “Oh, oh, what if…” was a common preamble to productive yet heady conversations with peers over zoom, as we scrambled together various visual representations in Miro and Figma.
This workflow has been essential to synthesizing content and a visual language for our video, which we’ve been iterating on through various stages of prototyping. I’m concerned about the overall fidelity and recognize that this will be important to suspension of disbelief for our intended audience — policymakers and various stakeholders connected to PPS must find this artifact compelling enough to act and bring these concepts into a shared reality.
On the technical side, video editing and motion graphics are computationally intensive tasks. I built a beefy workstation prior to starting at CMU, and this machine has been essential to so many tasks and assignments. Nevertheless, I’ve found that this work has strained my system’s capacity. I’ve purged files to make room for temporary caching and rendering outputs. I’ve reset my router in a desperate effort to speed up the transfer of data to Google Drive, and ran my system in a barebones state to maximize resources available to Adobe CC’s memory-hungry apps.
The stress I place upon the tools I use to design are complemented by the stress I’ve applied to myself. My sleep has been intermittent. I take short naps on the couch and found myself on more than one occasion this week working through the sounds of birds before the break of dawn. These late night hours are quiet and free of distraction, but tend to make the day that follows less than appealing. I’m staying awake through this last week of lectures, but finding my mind trailing off into thoughts about the timeline and how I might optimize frame rates for nominal render times. I’m obsessed with getting this video done, but know that this pace is not sustainable.
Week 13: Artifact Generation
We’ve began to generate assets for our final artifacts. This should be an exciting time for us. For the last 13 weeks, we’ve been living and breathing the problem space. The future of Portland Public Schools is not a matter of fate, it is something that will be built — not only designed, but also transformed by external forces and deliberate interventions. This work and our team’s research are only one tiny piece of this larger unfolding process, and we cannot know what impact (if any) will come from what we have done.
On some level, I cannot help but feel a little bit sad as we conclude this work. I have a very real sense of the scope of this issue and understand that fifteen weeks cannot generate anything conclusive. Nevertheless, we must honor this process and the deliverable. There is an underlying contradiction in this work. What this project calls for is “bold humility.” We know that our research is not conclusive, we also know that without bold presentation, we cannot inspire meaningful change or the greater vision by Prospect Studio.
Our primary concept is a news story about PPS holding their first ARC summit, and what it means for the future of Portland schools and teachers. We can use this medium to communicate the most salient details while glossing over the more bureaucratic aspects of our system level thinking. For secondary artifacts, we’re thinking about “swag” that is typical for a professional conference, as well as a custom logo for the ARC council.
I’m feeling a lot of pressure to resolve these artifacts to the highest fidelity possible. I know that the success of this project rests somewhat on our ability to persuade others, and we cannot know how this work will be interpreted if the artifacts are not convincing or feel too generic. I’m also worried that we have spent so much time working on the particulars that we haven’t given ourselves room for making these things.
I wish that we had a better sense of what is expected, and how craft will be factored into our grade. This is the first time that I’ve taken a studio class where nothing was made until the last two weeks. I expect that our team will be evaluated on the strength of our research and the clarity of our concepts, but as a studio class, I cannot shake this feeling that we should have been crafting prototypes along the way.
My hope for this week is that the momentum of making and the joy of purely creative pursuits will have a feedback effect to keep us motivated through this final push. I’m excited about the potential for the project even though we are still grappling with an incredibly high degree of uncertainty.
Week 12 Update: Evaluative Research Presentation and Reflection on Reaching The Project's Final Stage
This week our team presented our evaluative research to Prospect Studio (Fiona and other representatives were asynchronous for this session) and our guest, Arnold Wasserman. This presentation is the last before our final deliverable, and represents the conclusion of our research phase. While there are some loose ends for us to address (and further evaluation of our concept has not yet been attempted), we are now in the early stages of artifact synthesis.
The last few weeks have helped our team to understand the importance of user evaluation, what strategies do and do not work well in a remote/online context. In particular, we learned that building a survey is a miniature design project unto itself. The creation of an interactive system, and evaluating the results required significant labor up front and a lot of uncertainty throughout. Nevertheless, I feel that our team was successful in achieving specific goals.
I’m proud to say that we managed to get several different concepts in front of several educators from around the country as well as from within PPS specifically. We successfully navigated and sorted through feedback to gauge overall patterns of responses to several concepts as well as system-level evaluations. We managed to coordinate and divide our labor effectively, and communicated asynchronously as we brought key components together. This process was mirrored in the creation of our latest slide deck for Wednesday.
We received helpful feedback and challenges to our concept following our team’s presentation. As previously has been the case, our team had a good sense of who ought to respond to specific questions, since our divided labor has granted each team member some degree of specialization and familiarity with the topic we’ve been researching. Specifically, Arnold Wasserman was curious about how our artifacts could communicate these concepts in a compelling and persuasive manner. Arnold Wasserman pointed out that school boards and the people elected to them, have a tendency to be self-serving, to the detriment of the districts they represent. He questioned how our concepts would overcome the significant obstacle of implementation, especially given the fact that school boards and public officials hold the levers of power and the teachers are functionally an underclass in the United States.
This is something I’ve been thinking about since the beginning of this project, and I related back to these thoughts in response. My ideas are largely based on the work of Donella Meadows, and her famous essay on leverage points.
PLACES TO INTERVENE IN A SYSTEM
(in increasing order of effectiveness)
12. Constants, parameters, numbers (such as subsidies, taxes, standards).
11. The sizes of buffers and other stabilizing stocks, relative to their flows.
10. The structure of material stocks and flows (such as transport networks, population age structures).
9. The lengths of delays, relative to the rate of system change.
8. The strength of negative feedback loops, relative to the impacts they are trying to correct against.
7. The gain around driving positive feedback loops.
6. The structure of information flows (who does and does not have access to information).
5. The rules of the system (such as incentives, punishments, constraints).
4. The power to add, change, evolve, or self-organize system structure.
3. The goals of the system.
2. The mindset or paradigm out of which the system — its goals, structure, rules, delays, parameters — arises.
1. The power to transcend paradigms.
In particular, look at points three and four: the power to self organize and the goals of the system are key to understanding the forces necessary to reform PPS to more closely resemble the vision from Prospect Studio. I agree with Arnold Wasserman’s observation regard the school boards and policy makers, but I also see a real opportunity with this difficult and problematic group. They hold the levers, so we need only find a way to align their goals with the reforms we envisions for PPS.
If we accept the premise that politicians and school board members care about their own tenure and individual interests, and do so above all other considerations, then what we need to produce are artifacts that provokes the parents and registered voters of that school district. Once an activated and inspired public knows what they desire, they will vote for and ultimately elect representatives who promise to bring that vision to life. We have seen this on matters ranging from civil rights and infrastructure, to economics and war. Politicians will follow public pressure to keep their own seats warm.
Arnold seemed pleased with my answer, and suggested that our topic relates directly to the fate of our nation’s democracy — so, no pressure at all!
This weekend our team held three meetings to jumpstart this process of future artifact synthesis, and we have been more or less fruitful in this endeavor. It’s exciting to be in the final stretch, but our team has been struggling to maintain momentum lately. The demands of presentation weeks, and the rush to complete our research, often requires long hours, multiple zoom meetings outside of class, and many late nights. This has began to produce negative health consequences for our team.
We’ve been intensely looking at teacher burnout, but have also been confronted with the burnout of a pandemic, and the rigorous academics of a graduate program. Illness, headaches, and signs of exhaustion have crept into our team dynamic, and I’m concerned about what this will mean now that we are heading into the final push for this semester. What we really need at this stage is that spark of creativity and divergent thinking. It’s hard to do this level of work while also pushing up against the steady hum of stress and exhaustion.
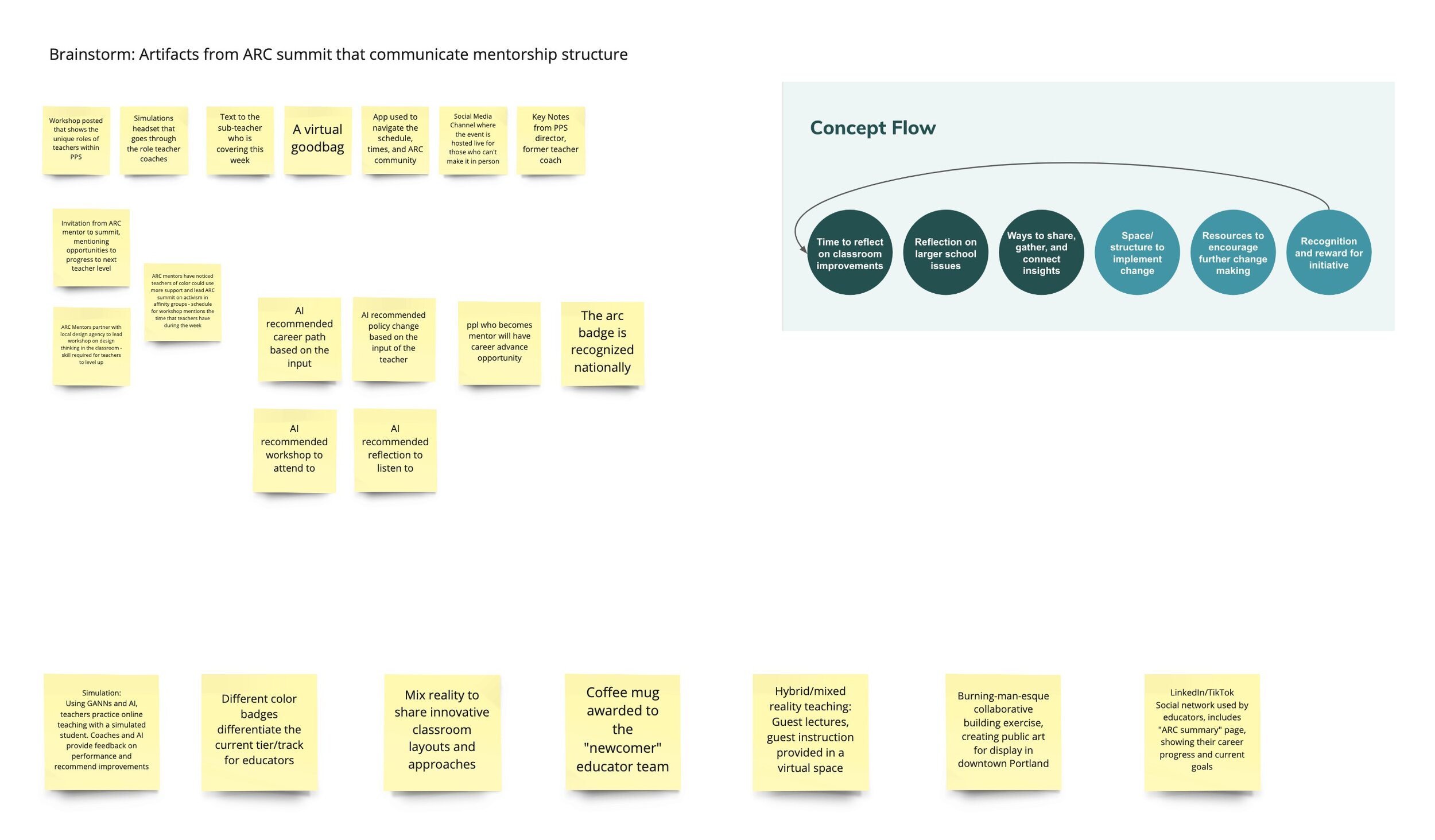
Brainstorming session, mapping events and trends to eventual implementation of key ARC concepts
I think it was a gigantic error on the part of CMU to breakup our spring break. I understand the rationale, and the concerns around travel, but this alternative strategy of giving students a random Monday or Tuesday off has not provided the benefits of time off to rest. I simply cannot “sleep faster” when given a 24 hour window, and I cannot catch up when one day of classes is omitted from an otherwise packed calendar. I’m burned out. I’ve got this strange ringing in my ear that won’t let up, and I’m having more trouble concentrating than at any other time this year.
Languishing in the fog of constant deadlines, constant tasks, constant meetings, constant emails, Slack messages, updates, etc., etc., have left me depleted. It has also sucked the joy out of doing this work. I hope this terrible mental and physical state doesn’t last, because I don’t see how I can be productive while feeling this way.
Week 11: qualitative evaluation of concepts
Our online survey is now underway, and while this virtual format isn’t exactly like so-called “speed dating,” we are hoping that it will be able to serve a similar purpose for our research. Creating a meaningful online experience for our participants was a tall order, especially with such tight constrains. There are many risks when created a fully automated and hands-off system. Not being there to clarify or to address questions or concerns in realtime was something we needed to accept as a trade-off. In exchange, we have a dozen unique participants ranging from 2 years to 27 years of experience, and from various districts around the country.
So far, the majority of responses have been from an online community of English teachers, so our data is skewed toward this perspective. On the plus side, English teachers provide excellent written responses. To avoid the pitfalls of statistics and quantitative analysis, we designed an online survey with open text fields, and we framed our questions around hypothetical scenarios. This would provide us with reflection and insights into how teachers imagine these concepts for themselves, and what perceived deficiencies come up for them in thinking about these systems in action.
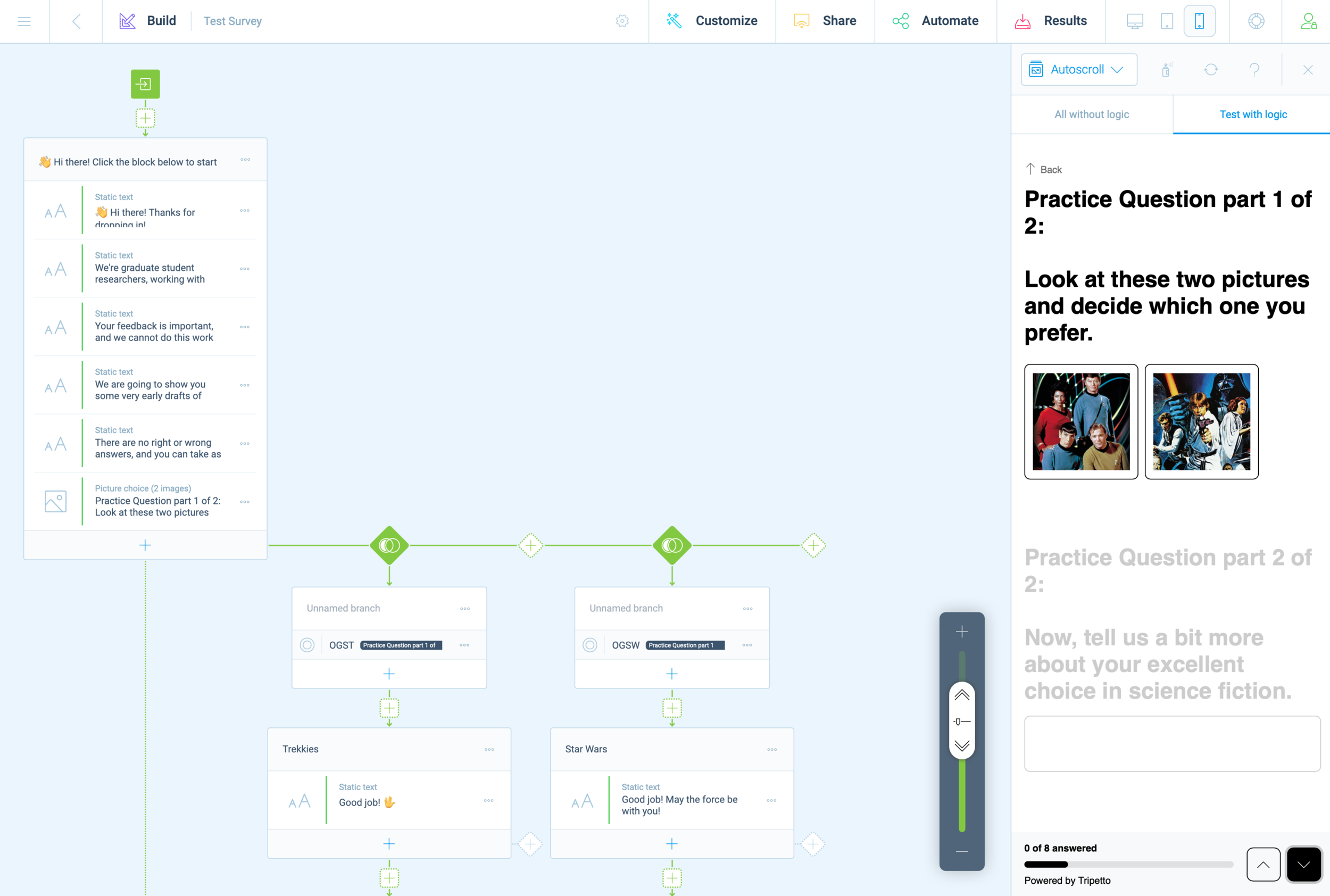
Screenshot of survey responses, exported into a CSV file
The last 24 hours in particular have been very exciting, as we finally gained access to online educator communities. This process has been slower than wanted, but we first needed to fully develop our survey before we could deploy it. This process in and of itself was a design challenge.
Last weekend, we decided to use the Tripetto platform. This gave us the same logic capabilities as TypeForm, but without any additional costs. It became clear almost immediately that we would need to prototype and refine our survey before receiving teacher feedback, and this effort was highly collaborative.
With multiple teammates, it was possible to divide this task into several areas that could be worked on independently and in parallel. We first decided on a basic structure and strategized the division of labor. Carol worked on the text/content based on a logic diagram we crafted together. While Carol crafted this outline, I created a mockup version in Tripetto. Without access to finalized concept sketches, I took some poetic license.
Screenshot of 2nd iteration prototype survey
As Carol and I worked together to refine the text copy, Cat and Chris worked together to create images and descriptive text for our participants. Once all of this content was ready for Tripetto, we began doing test runs, trying to break the experiences. This revealed some quirks with Tripetto’s logic functions and some of the less apparent features.
There are a few honorable mentions; Tripetto has a lot of subtle features that we often take for granted in other online experiences. Things like placeholder text, required fields, multiple choice radio buttons, checkboxes, multi and single-line text boxes. During the refinement phase, these features became essential and it was exciting to discover them—only after they were deemed essential enough to be worth the effort.
The minimalist UI of Tripetto made these features less evident, but not too hard to locate or execute. From start to finish, this experience felt a little shaky and uncertain but viable.
I often found myself this week grinding away on the platform, slipping into a state of mind that Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi describes as “flow.” In other words, creating a survey on Tripetto wasn’t easy to use, but just challenging enough to keep me interested in working through obstacles. I think that what helped support this effort the most was building models within platforms where everyone on the team is already fluent. For us, this was primarily Miro, Google Docs, and Sheets.
Screenshot of two representations of the survey, carried across platforms (Miro and Sheets)
First impressions matter, and we didn’t want to put out anything that wasn’t necessarily a work in progress. Even with this in mind, we did have a few last minute tweaks as we adapted our survey to maximize pulling power with other social media environments.
Arnold Wasserman’s desk critique was incredibly valuable for our team, as his feedback helped us to consider the importance of our survey as a communication tool. He recommended that we make the implicit, explicit, to directly communicate to our participants what we expected and why. We were encouraged to explain what questions we were asking, and to share this openly. This kind of transparency can be tedious, especially in text-based systems. I took this to task and simplified statements throughout the entire experience.
This gave the survey a personality all its own; like a casual and curious friend, we asked about specifics but with little pressure. We kept things open.
Open data cannot be calculated, it must be evaluated for patterns. Next week will be a scramble to synthesize patterns and new insights as we work to finalize system concepts into well defined parameters. We hope that through this process we will also identify opportunities to produce relevant and compelling artifacts (our final output/deliverable).
It still feels like a risk to be so far into a process and to still not have a clear idea of what it is we are making. We instead draw our assurances from what we have already made: an index of relevant articles, interview notes, countless diagrams and visual representations of high-level abstract concepts and maps at almost every level of visual fidelity imaginable, hundreds of presentation slides, dozens of pages of reflective text, and months worth of slack messages, shared links, and drafted emails. We created interactive digital workshop spaces and protocols for our participants, and archives with 256-bit encryption.
When looking at the collective volume of effort from this team, it’s difficult to imagine that we wouldn’t make something meaningful in the end. Is that too optimistic? Ask me in a month.
Week 10 update: Speed dating and concept evaluation
We had a somewhat irregular week for studio II. After our presentation, our team regrouped and strategized on how we might conduct the next phase of our research. We started out with just two concepts (an ARC educator “hackathon” and a community-promoting “ARC awards” program), and while our team felt confident that these concepts were feasible and desirable to addressing our problem space, we still had a lot of open-ended questions that would require further inquiry. Additionally, we became very concerned with the potential opportunity costs of not exploring more alternatives.
To address this concern, we decided to return to our primary research and synthesize niche problem statements that my provoke additional concepts. This went extremely well, and we now have more than a dozen concepts ready for evaluation. We’re excited to get these ideas in front of educators, but this remains to be a substantial obstacle to our process.
We consulted with Hajira and Sofia about our concerns, and asked how we might convert the highly synchronous activity of “speed dating” to a more online and asynchronous form. They recommended Typefrom and while this option was appealing, it came with a few drawbacks. The ultimate dealbreaker on this platform was the price. It costs $40 to enable the features that actually make the platform more useful than free products such as Google Forms. After some digging, I found a free alternative (they literally marketed themselves as such). Tripetto offers logic and branches that will enable our team to structure paths for our survey to tailor the individual experience. This is pretty huge, considering the scarcity factors our team has struggled with since the beginning of this project.
Despite this progress and excitement for next steps, I’ve personally struggled with motivation this week. I know that a lack of regular sleep and some external stressors are partially to blame, but there are many factors contributing to this. It’s been difficult to process (cognitively and emotionally) what comes next for me.
This week, I received my cap and gown, a diploma frame, and a few other artifacts to commemorate my time at CMU. I’ve been in school since January of 2014, and I feel incredibly lucky and grateful for this opportunity. To date, academics has been my longest career. I have spent more time being a student than my entire Navy enlistment, or my time working at Intel as an engineer. Each chapter came with its own struggles, failures, and success.
Each made an indelible mark on my psyche and personality. I could never imagine in my wildest dreams that my educational path would end here, in Pittsburgh, confined to my shoebox apartment, a deadly virus burning down countless lives while I indulge in high-level theories. I owe so much for this good fortune, and I do not know how I will ever repay the world for what it has given me.
It’s not so much that I am procrastinating — I put in a lot of hours this week, especially for this project — it’s that I’m paralyzed, afraid that what we are doing is missing something vitally important yet still unnamed. I also know that 15 weeks is hardly enough time to understand potential futures and their relationships to the current state.
It’s all crushing me down. I feel the weight of an obligation to deliver good work, yet terribly uncertain about this process. I’ve never done such intensive research before, and while I believe these theories and frameworks I’m soaking in (Worldview filters; Voroscone; Archplot structures; CLA; Empathy mapping; Participatory, Generative, Co-design, etc.) are helpful and necessary to our work, it’s difficult to know if the way our team applies these unfamiliar methods will yield truly impactful results.
I know that this is a learning experience, first and foremost it is an invitation to fail brilliantly as we discover new ways of making, but without any prior experience with this stage, it’s so difficult to keep my chin up and to believe in my own creativity and ability.
Week 9 Update: Presenting Generative Research Findings
Fiona Hovenden (of Prospect Studio) was back in class with us this week. Monday through Wednesday blurred together as our team worked around the clock to bring our findings into coherence. Through this process, we found that it was easier than past presentations for us to produce clear and concise summaries of our work. This outcome stems from two key advantages:
Our team continues to get better at coordination and understanding of each other’s strengths and weaknesses. This has accelerated our communication and the delegation of tasks.
As we continue living and breathing in this problem space, we have gained deep familiarity with core concepts and structures. This has allowed us to develop a kind of fluency in addressing Portland Public Schools as a topic.
There is still a lot that we do not know, but this is something which we must (as a matter of need) become comfortable accepting as a default state. There are limits to what we can and cannot know over a fifteen week period, with limited access to our stakeholders.
Nevertheless, we are slowly inching toward viable concepts.
These concepts are derived from last week’s workshops and diary studies. There was a lot of doubt and uncertainty going into our work last week, as we started with a zero participants. By Tuesday, all of this changed, and we found ourselves scrambling to coordinate with five different participants. Additionally, we coordinated with our counterparts (“Team Ahaa”) and I even took part in one of their workshops—after nearly 11 years of living in Portland, I had some qualified opinions to share.
This accelerated and compressed path from research to presentation ensured that we quickly moved from documentation to synthesis. Our team only had ten minutes to present all of this, and this constraint was helpful motivation to distill everything we learned over the last two weeks. So, what did we learn?
At a high level, generative research helped us to understand how educators see their relationship with various stakeholders. We gained more intimate, personal, and “day in the life of” perspectives from educators. We also got surprising feedback regarding their perception of possible futures. In general, there is not much hope for things improving substantially in the next ten years, but there is still a very real sense of urgency to make things better. This paradox has been with us since our first round of interviews but remains unresolved.
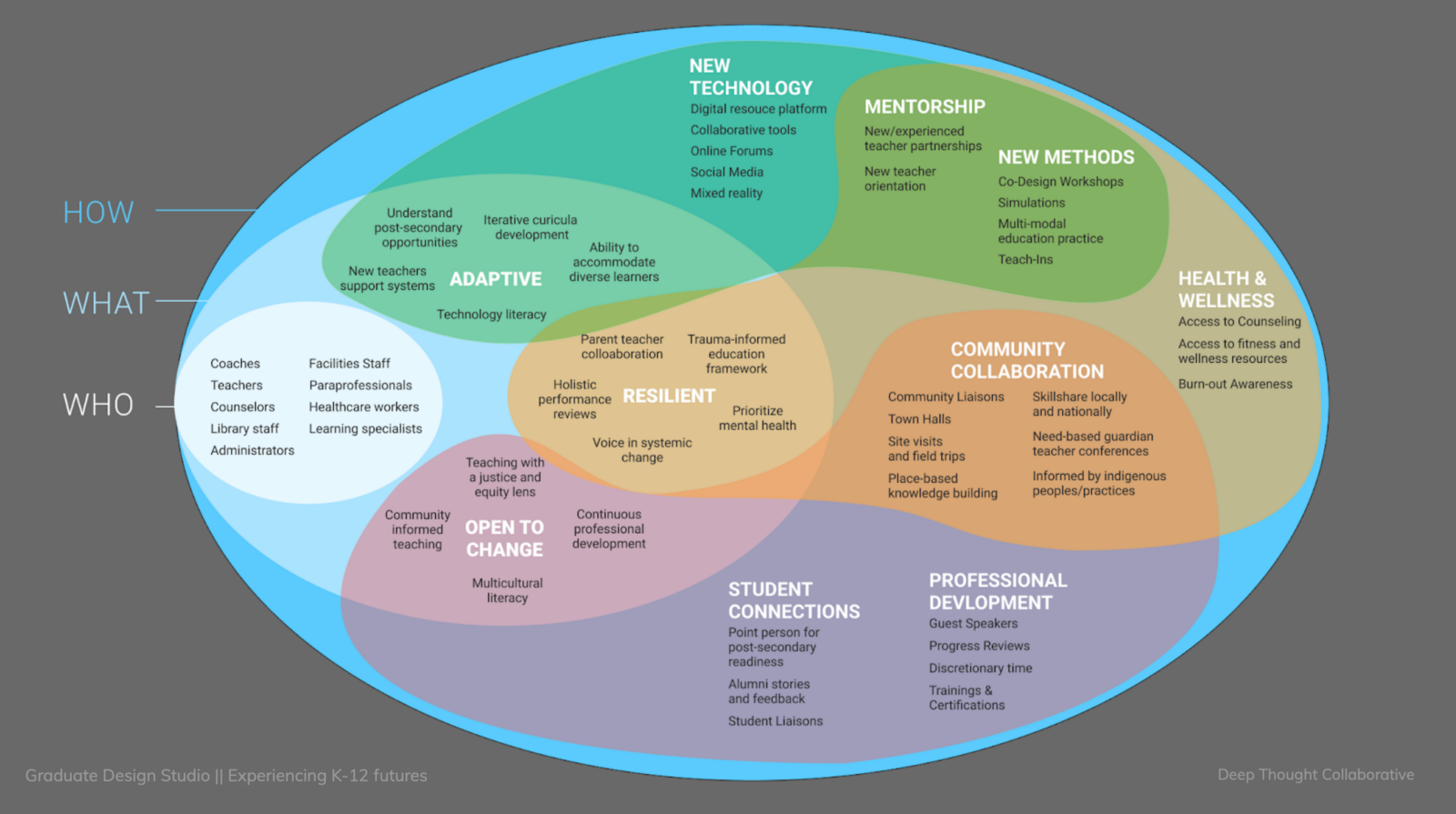
The most salient insights for our team were around issues of resilience and community:
Educators feel supported when colleagues show up and help proactively
Informal but reliable networks among educators support their resilience
Lack of resources and top-down surprises make teachers feel unsupported
Quality of life and mental health resources are poorly leveraged
“Empathy” and “Community” are other target areas in the Educator Essentials ring.
In our team’s presentation debrief, we had a lengthy discussion about this overlap, and our concerns about spreading ourselves too thin or not staying on target. This is an ongoing conversation and part of our general concerns for this project. We considered whether or not ARC is a “keystone” goal— resting on requisite conditions, and also essential to achieving other areas. This enmeshment is not entirely incompatible with the brief and Prospect Studio’s understanding of the problem space, but we must carry the burden of interpretation.
As we continue developing and evaluating concepts and potential interventions, we hope to achieve more focus on ARC, and to draw clear distinctions between outcomes and means to outcomes—e.g., is empathy an outcome of ARC, or is it a means to achieve ARC? This isn’t yet well defined, but I have faith in our team’s ability to resolve it.
Coming away from our Wednesday presentation, I can say that this task was both a relief and a source of pride. It was a huge relief to affirm key findings from Prospect Studio’s work, and also a moment of pride to have found these insights through workshops and protocols developed in house. This validated our research methods and demonstrated our core competency. Our protocols and assets were effective and entirely reproducible.
In terms of project management, we also took time to reflect on what was and was not working with our process and team contract. We do this every week as part of our “Rose, Bud, Thorn, and Shoutout” check-in exercise. We still felt more rushed than we’d preferred, and thought about ways to better support each other. We decided to designate “backup roles” to augment the facilitator and note-taker tasks. We hope that this will keep everyone equally engaged, while still offering flexibility and variety throughout the process. There are diminishing returns to these types of reforms, as we are already more than half way through the project. Nevertheless, every improvement counts.
Week 8 Update: Generative Research and Future Visions of Portland Public Schools
We began this week with a guest lecture from Adam Cowart, a PhD candidate in the transition design program. He introduced us to the concept of CLA (Causal Layered Analysis). We used this framework to better understand the landscape of our problem space at Portland Public Schools. Adam described different facets of the problem space through the lens of “litany filters.” To recognize what futures are feasible, we need to understand the triad of history, present, and future, and what elements in our landscape pull, push, or weigh down progress.
We took some time in class to reframe our insights through this framework, and began synthesis of potential elements to build a bridge toward the future vision created by Prospect Studio. This process began slowly, but after some heavy lifting we began filling out the diagram with great enthusiasm! It was refreshing to revisit our secondary research (which was already categorized under a STEEP-V framework). It was revealing to see visually how much further we have advanced our understanding of this problem space since literature review and background reading.
Outside of class, our team was busier than ever — working to adapt and overcome the obstacles we’ve encountered in our generative research phase has not been easy. I’ve struggled to support these efforts. The external factors of my personal and professional life have been an ongoing source of strain. I feel so much gratitude to the support and encouragement I’ve received from this team, and this week I felt a great deal of pressure to reciprocate.
Sample of generative research protocols
This effort to pay back the generosity I received (when I needed it most) began with a complete/comprehensive draft of our protocols for generative research, and the specifications for our workshop. Working with Carol, we delivered this to the team ahead of schedule. It was necessary for us to draft new protocols and workshop exercises to include a broader audience, outside of Portland Public Schools. We found that last week was somewhat of a dead end for seeking participation from our intended stakeholders (administrators and educators at PPS).
For our workshop, we wanted to know how different stakeholders perceive their relationships with counterparts, learn what different stakeholders prioritize and why, gain deeper understanding of how educators think about the future of public education, and to explore and define preferred futures.
We conducted three separate workshop sessions with educators outside of PPS. This included neighboring districts of PPS (Gresham-Barlow), as well as out-of-state educators. This approach allowed us to glean insights regarding that which is common in the US public school system, and that which is more specific to Portland. While this adaptation is not without its risks to skewed data, it is far more preferable that to remain without any additional insights beyond our primary research activities.
Screenshots of workshop activity
This was my first experience with executing participatory design with stakeholders and it has been such a rollercoaster of emotions. Since Carol and I worked on the protocol together, it was only logical that we also create the visual and interactive components for the workshop. We iterated on our initial concept by practicing with our own team, with each member taking a turn roleplaying as a participant. This helped us to work out the kinks and refine details before putting anything in the hands of our participants.
The first workshop with a real participant was very revealing. Having access to their thought process in real time, their visual associations, priorities, and ideas about the future were peeled back in layers, digging deeper into their lived experiences than we ever got through primary research and conversational interviews. Even the generation of simple sketches gave us glimpses into their inner worlds. I now question how important it was to conduct traditional interviews in the first place. Workshops are just so much more dynamic and active than interviews, and I consistently came away feeling more connected to the participants and their experiences.
This weekend was highly reflective. With new insights in hand, we spent over five hours evaluating what we discovered. There was so much for us to consider and it was only once we had the chance to pick it all apart together as a team that we could begin to make sense of it all. Many of our initial assumptions were blown out of the water. Our newfound perspective gave us a real sense of how important relationships are in the field of teaching. We also learned that technology is probably the least important factor for educators — with the exception of a desire for students to have high-speed internet at home, there was little to no interest in improving access to technology generally.
I’m still getting used to applying so many different approaches and methods so quickly. I feel like I’m only occasionally operating with a sense of clarity. There has been prolonged fuzziness that’s difficult to describe or ignore. It seems as though new insights provoke deeper questioning, while offering little in the way of certainty. I think this is just the experience of progressively revealing collective and individual ignorance. Before learning enough to act decisively, we must first gaze into the vast abyss of what we still do not know.
Week 7: Expanding scope of generative research
This week, our in-class sessions were dominated by guest lecturers who provided insights into our current work in progress. On Monday, Stacey Williams and Richard The asked us for our team’s “elevator pitch” and then asked us a few questions about the work we were doing:
Is the artifact(s) part of the intervention, or just a representation?
Is there a conceptual map that anybody should be working on to provide a system?
Can we design a process that will unify the decision making process at PPS?
Creating space where they can reflect on their own lives and experiences, and present a different model for education?
Carol was quick to respond regarding the relational mapping from our last presentation, and how our understanding of the relationships between administrators and other stakeholders has revealed a potential leverage point for meaningful interventions, but that the artifact should be something that inspires change.
Peter added that we’re separating the artifact from the process, but will develop an artifact that is representative of the depth of our research and understanding of the problem space. We then spent some time brainstorming out loud about some form of “ARC Institution” in the future could help to achieve the goals outlined in the Prospect Studio brief. A couple interventions we may want to prioritize:
Leadership development curriculum, teaching design and reflexivity.
Summer courses that are paid separately from the 9-month salary.
Peter reminded us that “future is fiction” and that it is our job as designers to bring that fiction into high enough fidelity that we make a persuasive argument through form. This ultimately means that we must situate the proposal within a fiction, and build from there.
Richard The wanted to know what other communication materials might inspire this. While not suggesting that we need to answer such questions with any degree of immediacy, we should put onto our horizon a few questions around how the ARC Institute might talk about these goals. For example, this could be a poster that says what life-long learning looks like.
Stacey’s other comments tied in well with the reading that Peter provided (Rutger Bregman). Specifically, this strange mismatch between education and the typical way we encounter work: i.e., in school, each subject is divided and compartmentalized, whereas in our work, often we must apply mastery of multiple subjects and do not have the luxury of flattening our problems into a single subject matter. Stacey pointed out that we (meaning educators, but also society) are boxed into binary thinking whereas other cultures have non-duality, non-binary ways of thinking.
Knowing that this entanglement is an obstacle to change, we must also consider what other sudden changes (from external factors, such as a pandemic or climate change) might present opportunities.
On Wednesday, Liz Sanders ran us through a series of role-playing exercises, where we considered the differences in priorities for stakeholders. This was confusing at first, but eventually we sync’d up and began negotiating as if we were in fact those different people in a school system. I was representing the thought process at a district level, while Carol played a student. I recognized that there were basic needs that were not at all address in our hypothetical scenario (a hackathon to create new and sustainable transportation for the future).
This was eyeopening and made our team think differently about our own approach to generative research…
Oh, our research. It has been challenging these last two weeks, and we’re worried about getting stuck. Despite so much cold calling/emailing acquaintances, we’ve found that right now in particular is a bad time to solicit any participation. PPS is migrating to a hybrid model, with teachers having stated a great deal of concern about safety. Additionally, this next week is their spring break, so any activities that require reflection on their daily lives will not capture work activity. This is also the only week of respite they will be afforded before summer break.
Nevertheless, there is some scintilla of joy to be extracted from this obstacle. I’ve had more motivation to reach out to people I haven’t been in touch with since graduation. Some of them are doing really great, others not. Some are starting families, others are starting careers. Much to my surprise, two acquaintances are actually in the process of becoming K-12 educators. This was not expected, but it was heartening to know that such alignments exist.
Our team is also struggling with external pressures: wrapping up mini courses, midterm expectations, job hunting and interviews, design challenges, personal struggles, and more. One of the things we specified in our team contract was transparency for such events. My team has been supporting me the best they can while I navigate these struggles and diversions. I too have been supporting them the best I can.
This weekend was very productive, as we generated new protocols and refined our workshop to included a broader range of participants. I’m especially excited to try out some of the techniques we’ve been considering, including: “Thing From The Future” based on the work of Stuart Candy, prioritization card sorts, and relational mapping. That last exercise was directly inspired by our conversation with Liz Sanders.
Thanks to a 20 oz. can of Red Bull, I was able to power through my very packed Wednesday, and I’m glad I made it that session, since we ended up monopolizing Liz in our breakout room — she seemed to be genuinely interested in our project, which was very, very humbling.
On the personal side of things, I’m glad to have my job interview and design challenge behind me. It’s been difficult to juggle so much, especially while still grieving the loss of a family member. I’ve been more emotionally raw, and feel less focused than I’d like. Some of this is due to a loss of sleep and not the workload. I seem to be “fine” during the day time, but when the sun sets, and the world gets quiet, I still think of him. I miss you, Uncle Ron. I’m sorry I won’t be there to send you to your final resting place. Like so many we’ve lost this year, you deserved better than this, and sending flowers to those left behind feels insufficient in the face of so much loss.
We’re about to cross the vital half-way mark in the semester. Normally this would include a spring break of our own, but due to concerns about increased student travel, we instead have pre-scheduled “off days” to (at least in theory) provide some periods of rest. It is something like having a nap instead of a full night’s sleep. We can make do, but that doesn’t mean we need to like it.
Week 6: Planning and coordinating generative research
“If we have to wait for the next pandemic to bring about big change, then we’re in big trouble!”
—Peter Scupelli
This week, our team presented our exploratory research findings with clients from Prospect Studio. This was something we did a “dry run” for the week prior. The feedback we received was generally very positive. In particular, I was pleased to learn that the “ARC” concept was aligned with the client’s understanding, and they even suggested that they would adopt this terminology for themselves! There was a lot of back and forth on this concept and it was incredibly validating. By recognizing the overlap and potential integration of these attributes (Adaptive, Resilient, and open to Change), and addressing them as a single verb, and not three distinct adjectives, we’ve reframed our inquiry to reflect actions and behaviors.
Fiona appreciated that we identified the multiple roles of educators who must address their own social and emotional needs, while also supporting students. She pointed out that teachers also need tools for communication.
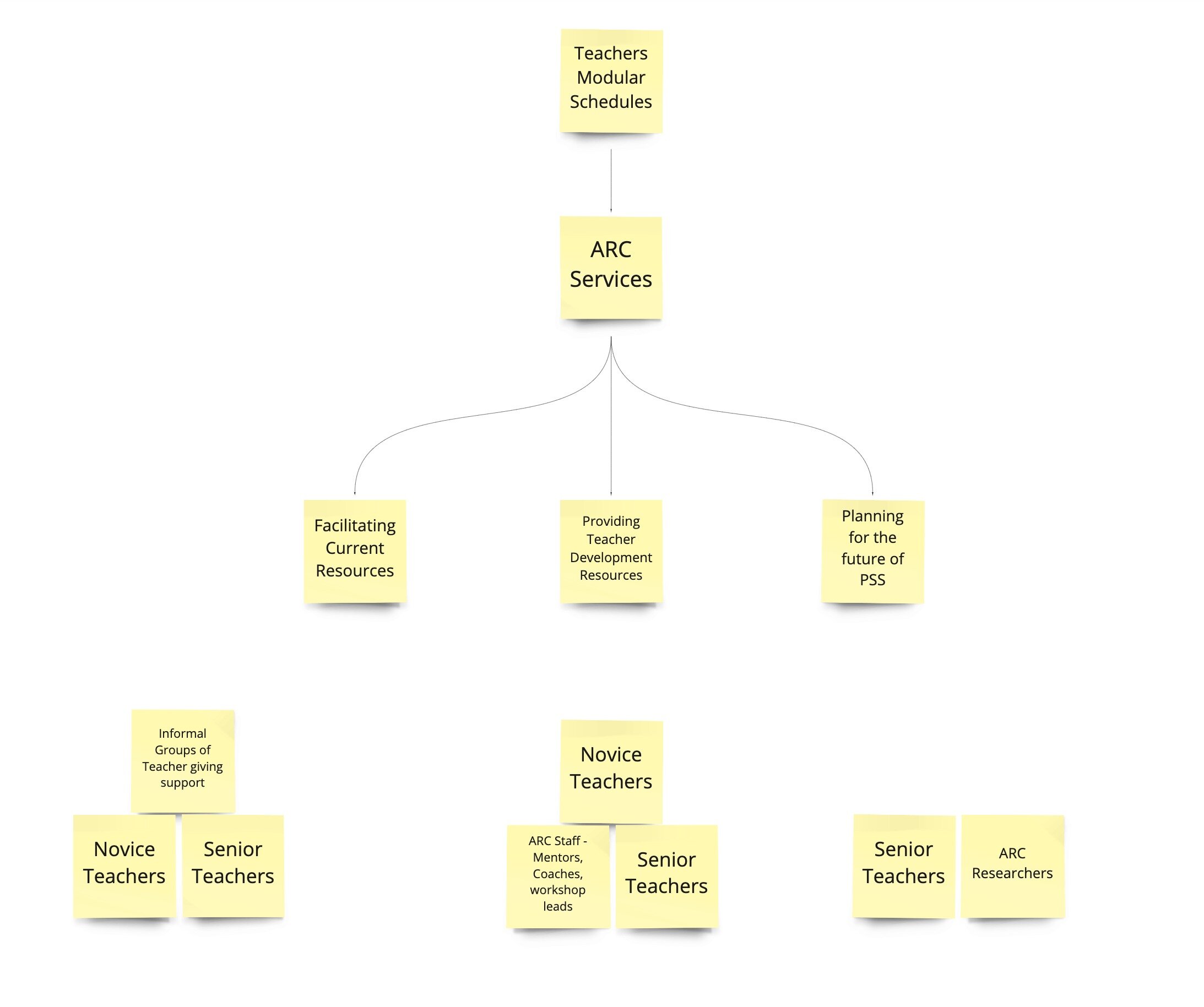
Collaboration Structure diagram was successful with Jenny Hoang. There was some confusion around Board members and their placement within districts. Carol was able to clarify this well for the entire team and I continue to be grateful for her contributions to the team. I’m very fortunate to be working with a team that has a nearly two year old working relationship— we’ve developed a beautiful shorthand together, and we recognize each other’s queues.
The administrators as a leverage point is something that both Jenny and Fiona resonated with, and this is promising for the next phase of our research. Jenny questioned our scope under the MLP. The national level might be too broad for some contexts, and there was a lack of distinction between state government policy makers and national/federal-level policy makers. This is something we will clarify going forward. Otherwise, the mapping of structured interactions was a huge success.
A question raised as we outlined this structure was what are the leverage points we’re considering, and what insights can we glean from the advent of COVID adaptations made to facilitate learning. We are doing a grand experiment in remote learning, but what are the lessons or takeaways from this experience?
We’re especially interested in the role technologies in facilitating communication. Video conferencing is only one small part of this. Thinking about organizational structures, we want to improve the modes and means of communication between administrators, educators, and other stakeholders. During our critique, Cat explained that open communication presents problems under a framing that leads to practical solutions. Being able to express needs for things like a mid-day break can have a profound impact on the quality of life for educators day-to-day. Jenny concurs and believes from her experience with exploring PPS that there is a lot of desire around this realm.
After our Wednesday workshop, our team met to discuss these important next steps. It was also Cat’s birthday!
We had a good time, but still got a lot of work done! We had some imbalance in the distribution of work, preparing for this presentation, and we’ve amended our team contract to (hopefully) improve delegation of future tasks. We’re also rethinking the responsibilities for team members who are not assigned facilitator or notetaker for a given week. One challenge is that some tasks end up being more involved than originally thought. When splitting up the work, it can be like cutting a pizza while blindfolded: everyone gets a slice, but there’s no guarantee that those slices will be anywhere near the same portion. In the future, when we find out that we got a too big or too small of a task, we can further split and breakdown tasks (where possible) to keep everyone productive but not overburdened.
After addressing our coordination for this next phase, we began mapping our current questions and considering what we wanted to learn. What we realized through this exercise was that almost any available method of active research could provide insights to our questions, so we simply needed to prioritize what would work best for us and work from there to design experiences that will illuminate these areas.
Our next steps will include generative research and workshops, and our hope is to gain more insights into this aspect of interpersonal and organizational communication. Through our primary research, and framing under ARC, we’ve identified a few key aspects of effective communication:
Problem-solving mindset
Active listening
Maintaining open communication and feeling heard
Other areas of consideration collaboration structures:
How do educators coordinate their efforts to bring change?
How do they support or hinder adaptations or changes?
What visions do administrators see for the future of PPS, their roles, and the roles of educators?
Peter recommended that we also consider future contexts, and think about relevant trainings and preparation. Pandemics are not frequent, but when COVID-19 arrived, there wasn’t any plan in place. This put districts in an especially difficult position—reacting to sudden change is never easy, and they had no prior practice. Other sectors (especially government sectors) often need to prepare for scenarios that are unlikely to happen but are potentially very disruptive.
Thinking about this point remind me of a very grim reality, that school shootings in the United State have become so frequent that schools began holding drills. I was a high school student in 1999, when Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold committed a horrific massacre at Columbine High School in Colorado. It’s difficult to describe what a profound impact this had on my experience with public education. Growing up as a teenager in rural Utah, the proximity to this tragic event resulted in an immediate reaction. My school began conducting “random” locker searches. Teachers and counselors began interrogating students media consumption—at that time, it was believed that playing DOOM and listening to Metallica were red flags.
As a community, what we needed were meaningful policies. Instead, we were subjected to onerous and disruptive security measures, derived from alarmist and factually inaccurate claims. Their response didn’t prevent such tragedies, but they did add to the hardship of students who were already terrorized. School shooting drills have not made today’s kids any safer, because the root cause remains unaddressed. We needed policy then, and we need policy now.
Good policy, however, is only possible when there is a clear understanding of the problem. An important role of a vision of the future is to anticipate needs before they become a crisis. This can lead to preventative policy and proactive measures. To understand the present, we need to also understand the past. To understand the future we need to understand the present. To gain deeper insights beyond interviews, we’re planning to start participants with a cultural probe diary study (this might be in their chosen format or sent daily by us) and then bring a mix of administrators and teachers into a workshop.
We’re still working out the details, but our current favored approach is the “Draw Toast” exercise.
We’re nearly done with our protocols and will be contacting our participants on Monday. I’m curious about what will be confirmed (from our exploratory stage) and what will be new or contradictory to our current understanding. We’re now focusing on something specific, but there are degrees of assumption going into this next step. I’m excited (and a little nervous) to learn more from our participants and to benefit from their lived experiences.
Week 2: Portland Public Schools Territory Mapping, Personal Reflection
“It always seems impossible until it’s done.”
—Nelson Mandela
On Wednesday we presented our territory maps to the class and Fiona—our guest from Prospect Studio. From completing the MA last year, and my work in the Service Design seminar course, I feel somewhat confident in the quality of our combined efforts and the contributions I personally had to offer. We worked through several iterations, and presented our first draft on Monday for Peter’s review. The feedback we received was helpful. In particular, Peter asked that we include systems level goals, specify equity-centered outcomes, and leverage personas and vignettes to aid in narrowing to a single area of focus. We were also encouraged to focus our primary and secondary research on the current state of things at PPS.
First Draft territory map, as it was presented on Monday
Stef recommended that we begin our presentation with an explanation for why we chose PPS and our chosen area of focus. Thinking about how we might explain these choices revealed for our team how these different aspects are connected, and to being recognizing some common threads. On Tuesday our team met for an informal work session. These kinds of meetings have been very helpful in keeping us on track and motivated—especially during this prolonged quarantine, working independently can be a real drag. Working together remotely and having realtime communication with one another has also been useful in ensuring we reach consensus on key decisions.
For example, at the beginning of our meeting on Tuesday, we spent roughly fifteen minutes clarifying our intentions, area of focus, and defining the various terms outlined in the brief: what does it mean for an educator to be “resilient, adaptive, and open to change”? This was important for the next phase of refining our territory map. We converged from exploring three distinct areas in the brief to a single section (educator essentials). We decided on a general format for the territory map (based on examples shared by Hajira’s morning presentation) with “who,” “what,” and “how” as distinct categories, arranged from inside-out. Initially, the concentric arrangement proved limiting. Our team opted to transition to an elliptical arrangement, exploiting the typical 16:9 widescreen format.
While I cannot speak for the entire team, I am most proud of our willingness to embrace ambiguity and to continue working through high degrees of uncertainty, toward something more coherent. I have no doubt that the outcome of our collective efforts were far superior to anything we could have made by working individually. Our collective intelligence was on display Wednesday, and it seemed that Fiona and Peter were pleased with the work.
Ultimately, we produced a fairly comprehensive map; this first deliverable represents many different perspectives, and our combined understanding of the brief. We managed to produce something that is visually appealing, and which communicates our ideas on this topic. There is still quite a bit of work to be done before we can validate these categorical relationships, but our team was very successful at representing the current state of our research, and how our process will unfold over time.
Final draft of our team’s territory map, as presented on Wednesday.
One unsettled question: how can we maximize the impact of our field research and ethnographic approach in the context of a pandemic? We shared a few options, and while we could not settle on an exact methodology just yet, we did agree to pool our resources and purchase some small tokens of gratitude. This was inspired—through personal experience with volunteering, I know that “thank you” goes much further when it includes a tasty treat or tangible artifact to commemorate the experience.
We met again this weekend and debriefed on our experience with the presentation. We continued working in a variety of collaborative digital environments and management tools (Figma, Trello, Miro, Google Docs, Slack), but upon Chris’ recommendation, we have decided to add another tool to the mix: Framer. Our team contract remains intact at this time, but we amended our debriefings to include a “rose, bud, thorn” framing. This made it much easier for the team to share their thoughts and feelings about the work so far. We also added a “shoutout” option for meaningful expressions of gratitude. This worked very well for our first debrief, and will likely be standard going forward.
The Future of Portland Public Schools — Week 2, Team Update
This week, our team posted a bio on our course homepage. Chris put it best, “we cute as hell, just saying:”
Making the best of remote collaboration
We also drafted a team contract to establish expectations and roles, among these are:
Goals for this project:
Sharpen our skills for…
Research-based design
Remote collaboration
Providing meaningful artifacts for a client
Something great for our portfolios
Expectations
Meetings scheduled to avoid conflict and maximize productivity
Established deadlines
Delegation of tasks
Regular updates and communications for peers
Time to celebrate accomplishments
Policies:
Commitment to ongoing research to strengthen and refine ideas, concepts.
Flexibility and understanding (because there’s still a pandemic and bad things can and will happen)
Consequences and conflict:
Call people in, not out. If something is not going well, we all have a problem and can work together to solve it.
Transparency: let’s communicate when there are problems, we all have valuable perspectives and may recognize something that others do not
When possible, table discussions if we cannot easily make decisions. Decide when/if to address problems as a group or between group members
Custom rules for meetings:
Rotation of responsibilities so folks don’t burn out on repetitive tasks.
In addition to structuring our collaborative efforts, we also completed a first draft of our research team’s territory map.
First draft version of territory map for PPS, based on the brief provided by Prospect Studio
Our professor, Peter Scupelli provided feedback on our initial presentation draft:
Need to include systems level goal
Need to specifically include equity-centered systems and outcomes
Leverage personas and vignettes to aid in choosing area of focus
Recommend researching the current state with a focus on equity
To improve the focus and process of our research, we’re also reviewing text from How To Future, a book by Madeline Ashby and Scott Smith. Chapter 3 describes the process for sensing and scanning information, which will be useful for our secondary research and literature review, as well as synthesizing insights from primary research and participant interviews.
Since the scope of this project is fairly broad and also because we are working on it for 15 weeks, we’ve also decided to adopt the project management tool, Trello to aid us in tracking our individual and collective progress, assign/delegate tasks, and note passing key milestones.
Using the feedback we received from our professor and our excellent TA, Sefania La Vattiata, we set more specific goals for completing our territory map.
Summary of Decisions/Surfacing Perceived Alignments:
Converged from 3 slices to one sections of the outcomes. Current Territory Map should focus exclusively on Educator Essential: Adaptive, resilient and open to change
To frame our future, we are currently considering the possibilities and methods that adults can learn how to partner with students about what happens after graduation/their long term goals
New Format for territory map based on Hajira’s work. From the center outward: Who-> What -> How -> Future experiences
Future experience should be structured within the futures scenario we are currently exploring
For the future experiences outer most rim, each scenario ideally aligns with an accompany assumption or question about the present. ie Future: VR explorations of proposed new school house Past: How/Can people see these plans today?
To do list for Wednesday’s Presentation:
Update deck with new (1) focus, (2) research, (3) Territory Map/Reasoning
Add Section in the deck about for the proposed Future Scenario we are exploring
Deck should be finished no later than Wednesday at 11am, share any changes
Which area are we truly focussing on? Educator Essentials? Graduate Portrait? We’re a bit hung up on the adaptive, lifelong learning? Our hope is that through this process, it will be easier to narrow our focus to the educator essentials.
UPDATE:
Our team completed their second revision of the territory map for the Educator Essential vision of Adaptive, Resilient, and Open to Change.
Reflecting on the first week (Studio II and Research Methods)
On Monday we kicked off a design research project for Studio II. Peter began the brief with a quote:
“We see things not as they are, but as we are.”
—H.M. Tomlinson, Out of Soundings
This has stuck with me throughout the week as our team began exploring two public schools for consideration of focus. Portland Public Schools are an obvious choice because I bring unique insights to this domain—I have a couple years experience volunteering at Ockley Green K-8 and NAYA’s after school youth mentorship program. I’m able to contribute lived experience and perspective. I know PPS educators and know many of the challenges they face. I also feel very much indebted to this community, as they opened their doors to me and helped me at a critical stage of my journey into the field of design. It is my sincerest wish and goal to contribute to a more positive future for the children of district.
Having reviewed the briefs for Portland Public and for Santa Clara, I am reminded of the work I did over the previous summer, interning as a communication designer for Dezudio (Ashley and Raelynn’s design studio, here in Pittsburgh). This was a fantastic opportunity to apply recently acquired skills and knowledge from service and communication design coursework to address the challenges of Brooklyn LAB Charter School in the context of COVID-19. Central to this work was understanding the needs of historically marginalized communities which already could be described as “in crisis.” These conditions were amplified by COVID-19, but also presented an opportunity to justify significant overhaul to this institution and their approach to supporting student’s academic needs.
I’m excited to work with our assigned team. Cat, Caro, and Chris were all members of our MA cohort, and we have good rapport from previous projects and our time together in the studio. Additionally, this team comprises of a plurality of individual experiences and perspectives. Cat attended a private school in D.C., Carol is from Taiwan and has no direct or personal experience with public education in the United States. Chris and I both come from hyper-conservative and religious homes, and this impacted the way in which our parents made choices regarding education. For Chris, this meant a combination of home schooling as well as traditional enrollment. For me this meant several gaps and educational deficiencies (e.g., attending a rural school district with trailers in lieu of a school building) and eventually dropping out altogether. I did not finish high school, and instead passed the G.E.D. when I was still seventeen years old. These experiences lend to a strong negativity bias on my part, which I hope will balance out some of the more optimal experiences of my peers—I know all too well what doesn’t work in public education.
For the first week of our Research Methods course, we read excerpts from Alan Cooper and a paper by Branka Krivokapic-Skoko. A few points I found helpful from Cooper:
I agree with many sentiments, but his definitions for design, expertise, stakeholders, and just the entire framing of “users” feels very outdated.
I’m not sure that I agree with him on this statement:
Users of a product should be the main focus of the design effort.
I take issue with this framing because, as Cooper points out, the user is not always the same person as the customer. This is certainly the case in public schools, where students are not paying for a service, but still have specific needs. And are students “users” of a product? This market-based framework seems much more useful in a for-profit context.
When he says that, “it is important to speak to both current and potential users, that is, people who do not currently use the product but who are good candidates for using it in the future because they have needs that can be met with the product and are in the target market for the product” I question why this is the goal. Is it good to grow the market for growth’s sake? What if I’m designing iron lungs and that JERK Salk is trying to push me out of the market?
Product and competitive audits: Also in parallel to stakeholder and SME interviews, it is often quite helpful for the design team to examine any existing version or prototype of the product, as well as its chief competitors.
This one seems pretty obvious, but last semester it was also very important that our research include lots of exploration into the same product/system space. Knowing what is out there helped us to recognize new potentials for existing applications and solutions.
On Wednesday, Stef (our TA for the class) shared her team’s project to give us a better sense of what to expect in terms of process and crafting our deliverables. This was useful for priming ideas about how to approach the somewhat open-ended prompt to create an artifact to represent daily life for PPS in the year 2035. Based on this impression, I began thinking about individual goals for this project and thinking about what I can hope to improve or learn throughout this process:
Remote collaboration
Research-based design
Providing meaningful artifacts for a client
Producing something great for a portfolio
I inserted these items into our team contract. For Monday, we need to complete a first draft territory map for PPS. This process has been a bit slower, and Cat mentioned how much she misses having access to a physical whiteboard. Even though we’ve been working in this “new normal” for nearly a full year, it is impossible to ignore what we have lost by switching to a remote learning context.