This week our team presented our evaluative research to Prospect Studio (Fiona and other representatives were asynchronous for this session) and our guest, Arnold Wasserman. This presentation is the last before our final deliverable, and represents the conclusion of our research phase. While there are some loose ends for us to address (and further evaluation of our concept has not yet been attempted), we are now in the early stages of artifact synthesis.
The last few weeks have helped our team to understand the importance of user evaluation, what strategies do and do not work well in a remote/online context. In particular, we learned that building a survey is a miniature design project unto itself. The creation of an interactive system, and evaluating the results required significant labor up front and a lot of uncertainty throughout. Nevertheless, I feel that our team was successful in achieving specific goals.
I’m proud to say that we managed to get several different concepts in front of several educators from around the country as well as from within PPS specifically. We successfully navigated and sorted through feedback to gauge overall patterns of responses to several concepts as well as system-level evaluations. We managed to coordinate and divide our labor effectively, and communicated asynchronously as we brought key components together. This process was mirrored in the creation of our latest slide deck for Wednesday.
We received helpful feedback and challenges to our concept following our team’s presentation. As previously has been the case, our team had a good sense of who ought to respond to specific questions, since our divided labor has granted each team member some degree of specialization and familiarity with the topic we’ve been researching. Specifically, Arnold Wasserman was curious about how our artifacts could communicate these concepts in a compelling and persuasive manner. Arnold Wasserman pointed out that school boards and the people elected to them, have a tendency to be self-serving, to the detriment of the districts they represent. He questioned how our concepts would overcome the significant obstacle of implementation, especially given the fact that school boards and public officials hold the levers of power and the teachers are functionally an underclass in the United States.
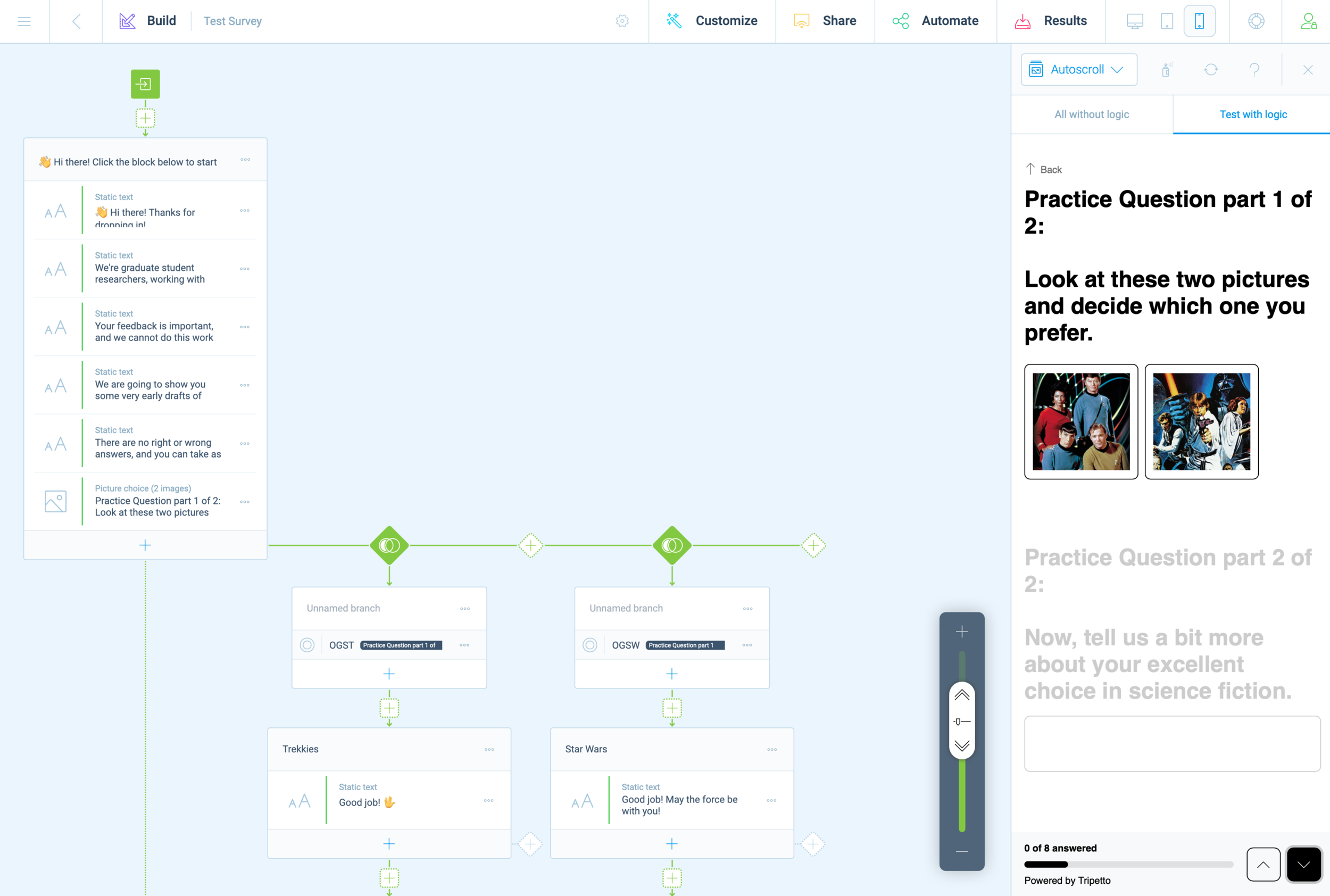
This is something I’ve been thinking about since the beginning of this project, and I related back to these thoughts in response. My ideas are largely based on the work of Donella Meadows, and her famous essay on leverage points.
PLACES TO INTERVENE IN A SYSTEM
(in increasing order of effectiveness)
12. Constants, parameters, numbers (such as subsidies, taxes, standards).
11. The sizes of buffers and other stabilizing stocks, relative to their flows.
10. The structure of material stocks and flows (such as transport networks, population age structures).
9. The lengths of delays, relative to the rate of system change.
8. The strength of negative feedback loops, relative to the impacts they are trying to correct against.
7. The gain around driving positive feedback loops.
6. The structure of information flows (who does and does not have access to information).
5. The rules of the system (such as incentives, punishments, constraints).
4. The power to add, change, evolve, or self-organize system structure.
3. The goals of the system.
2. The mindset or paradigm out of which the system — its goals, structure, rules, delays, parameters — arises.
1. The power to transcend paradigms.
In particular, look at points three and four: the power to self organize and the goals of the system are key to understanding the forces necessary to reform PPS to more closely resemble the vision from Prospect Studio. I agree with Arnold Wasserman’s observation regard the school boards and policy makers, but I also see a real opportunity with this difficult and problematic group. They hold the levers, so we need only find a way to align their goals with the reforms we envisions for PPS.
If we accept the premise that politicians and school board members care about their own tenure and individual interests, and do so above all other considerations, then what we need to produce are artifacts that provokes the parents and registered voters of that school district. Once an activated and inspired public knows what they desire, they will vote for and ultimately elect representatives who promise to bring that vision to life. We have seen this on matters ranging from civil rights and infrastructure, to economics and war. Politicians will follow public pressure to keep their own seats warm.
Arnold seemed pleased with my answer, and suggested that our topic relates directly to the fate of our nation’s democracy — so, no pressure at all!
This weekend our team held three meetings to jumpstart this process of future artifact synthesis, and we have been more or less fruitful in this endeavor. It’s exciting to be in the final stretch, but our team has been struggling to maintain momentum lately. The demands of presentation weeks, and the rush to complete our research, often requires long hours, multiple zoom meetings outside of class, and many late nights. This has began to produce negative health consequences for our team.
We’ve been intensely looking at teacher burnout, but have also been confronted with the burnout of a pandemic, and the rigorous academics of a graduate program. Illness, headaches, and signs of exhaustion have crept into our team dynamic, and I’m concerned about what this will mean now that we are heading into the final push for this semester. What we really need at this stage is that spark of creativity and divergent thinking. It’s hard to do this level of work while also pushing up against the steady hum of stress and exhaustion.